Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 3.1 What is a Utility Map?
- 3.2 The Significance of Utility Maps: Unlocking a World of Benefits
- 3.3 Types of Utility Maps: A Spectrum of Options
- 3.4 Creating a Utility Map: A Systematic Approach
- 3.5 FAQs about Utility Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effectively Using Utility Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: Utility Maps – A Foundation for Efficient and Safe Infrastructure Management
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
![GIS for Electric Utilities [The Ultimate Guide] GIS Cloud](https://www.giscloud.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GIS-for-Electric-Utilities-electric-utility-asset-management-software-1024x589.png?x35544)
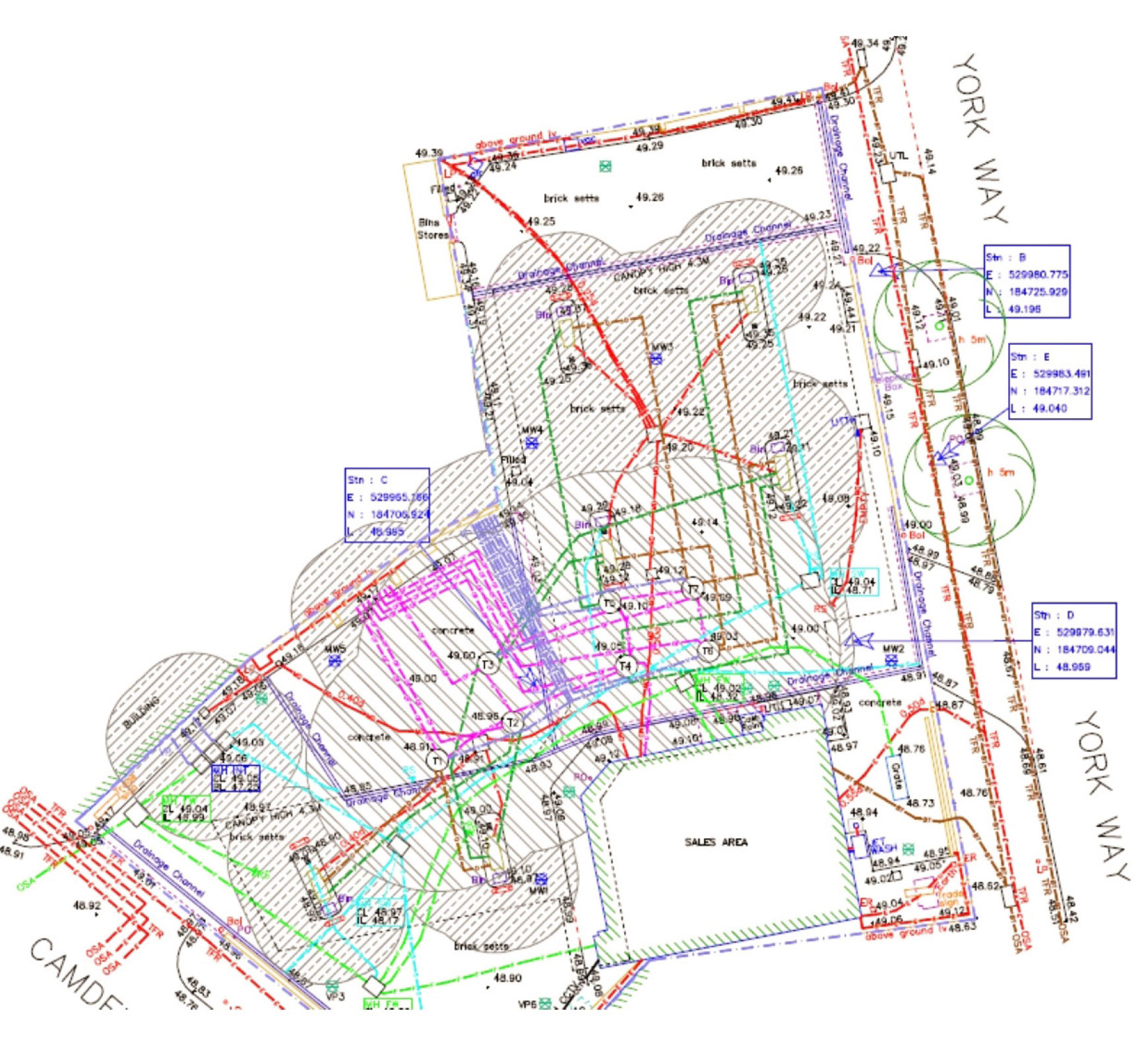
In the intricate tapestry of modern infrastructure, the seamless flow of essential utilities like electricity, gas, water, and telecommunications is paramount. Ensuring this flow requires meticulous planning, coordination, and an understanding of the complex network that lies beneath our streets and buildings. Enter the utility map, a powerful tool that provides a visual representation of this intricate web, empowering stakeholders to navigate and manage utility infrastructure effectively.
What is a Utility Map?
A utility map is a detailed graphical representation of the location, type, and characteristics of underground and overhead utility infrastructure. It serves as a comprehensive guide to the network, encompassing elements such as:
- Location: Precise coordinates of utility lines, pipes, and conduits, often displayed on a geographical base map.
- Type: Identification of the specific utility (e.g., electricity, gas, water, telecommunications) and its associated components.
- Depth: Indication of the depth at which utilities are buried, crucial for excavation and construction projects.
- Material: Specification of the materials used for pipes, cables, and conduits, providing insights into their properties and potential hazards.
- Ownership: Identification of the utility company responsible for each infrastructure element, aiding in coordination and communication.
The Significance of Utility Maps: Unlocking a World of Benefits
Utility maps play a pivotal role in various sectors, offering a wide range of benefits that contribute to efficient and safe operations:
1. Safety and Risk Mitigation:
- Preventing Accidents: By providing a clear visual representation of underground infrastructure, utility maps help avoid accidental damage to utility lines during excavation, construction, or maintenance activities. This significantly reduces the risk of service disruptions, injuries, and costly repairs.
- Identifying Potential Hazards: Utility maps highlight the presence of hazardous materials, such as high-voltage cables or flammable gas lines, enabling stakeholders to take necessary precautions during operations.
- Emergency Response: During emergencies, such as power outages or gas leaks, utility maps facilitate rapid identification of the affected infrastructure, enabling swift and targeted response efforts.
2. Enhanced Planning and Coordination:
- Infrastructure Development: Utility maps serve as essential tools for planning new infrastructure projects, ensuring that proposed developments do not conflict with existing utility lines. This minimizes delays, cost overruns, and disruptions to existing services.
- Maintenance and Repair: Utility maps facilitate efficient maintenance and repair operations by providing detailed information on the location, type, and condition of utility infrastructure. This allows for targeted interventions, reducing downtime and minimizing service disruptions.
- Network Optimization: By analyzing utility maps, stakeholders can identify areas for network optimization, such as upgrading infrastructure or expanding capacity to meet growing demand.
3. Improved Communication and Collaboration:
- Shared Information: Utility maps provide a common platform for sharing information about utility infrastructure among different stakeholders, including utilities, contractors, developers, and government agencies. This fosters transparency and facilitates effective collaboration.
- Stakeholder Coordination: Utility maps enable stakeholders to coordinate their activities effectively, minimizing the risk of conflicts and ensuring the smooth execution of projects.
- Regulatory Compliance: Utility maps are often required by regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with safety standards and environmental regulations.
4. Cost Reduction and Efficiency:
- Reduced Excavation Costs: By avoiding accidental damage to utility lines, utility maps significantly reduce excavation costs associated with repairs and rework.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Utility maps facilitate efficient resource allocation by providing insights into the location and condition of utility infrastructure, allowing for targeted maintenance and repair efforts.
- Improved Service Delivery: By minimizing disruptions and optimizing operations, utility maps contribute to improved service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Types of Utility Maps: A Spectrum of Options
Utility maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and applications:
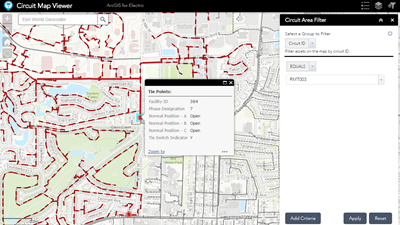
- Digital Utility Maps: Utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology, digital utility maps provide interactive and dynamic representations of utility infrastructure. These maps offer advanced features such as data layers, spatial analysis, and real-time updates.
- Paper Utility Maps: Traditional paper maps provide a static representation of utility infrastructure, often used for planning, maintenance, and emergency response.
- Hybrid Utility Maps: Combining the benefits of digital and paper maps, hybrid utility maps offer a balance between interactivity and accessibility.
Creating a Utility Map: A Systematic Approach
The creation of a utility map involves a systematic process that ensures accuracy and completeness:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including utility companies, historical records, aerial imagery, and field surveys.
- Data Verification: Verifying the accuracy and consistency of collected data to ensure the reliability of the utility map.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from different sources into a unified system, creating a comprehensive representation of utility infrastructure.
- Mapping and Visualization: Displaying the integrated data on a geographical base map, creating a clear and visually appealing representation of the utility network.
- Data Maintenance: Regularly updating the utility map to reflect changes in infrastructure, such as new installations or repairs.
FAQs about Utility Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the different data sources for creating a utility map?
Data sources for creating a utility map can include:
- Utility company records: Utility companies maintain detailed records of their infrastructure, including location, type, and depth.
- Historical records: Existing maps and plans from previous projects can provide valuable insights into the location of utility infrastructure.
- Aerial imagery: Aerial photographs and satellite imagery can be used to identify overhead utility lines and locate underground infrastructure.
- Field surveys: Ground-based surveys using GPS and other instruments provide accurate measurements and detailed information about the location and characteristics of utility infrastructure.
2. What are the common challenges in creating and maintaining utility maps?
Challenges in creating and maintaining utility maps include:
- Data accuracy and consistency: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data from different sources is crucial for the reliability of the utility map.
- Data accessibility and sharing: Obtaining access to utility data from various sources can be challenging, especially in cases where information is not readily available or requires permission.
- Data updates and maintenance: Keeping the utility map up-to-date requires ongoing efforts to incorporate new data and reflect changes in infrastructure.
3. What are the best practices for using utility maps?
Best practices for using utility maps include:
- Regularly updating the map: Ensuring that the utility map is up-to-date with the latest information on infrastructure changes.
- Using the map for planning and decision-making: Integrating the utility map into all stages of planning, construction, and maintenance activities.
- Sharing the map with relevant stakeholders: Ensuring that all relevant parties have access to the utility map to facilitate collaboration and communication.
4. What are the future trends in utility map technology?
Future trends in utility map technology include:
- Integration with 3D modeling: Creating immersive 3D models of utility infrastructure to provide a more comprehensive and realistic representation.
- Real-time data updates: Incorporating real-time data feeds from sensors and other monitoring systems to provide dynamic updates on infrastructure status.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Utilizing AI and ML algorithms to automate data analysis, identify patterns, and optimize utility operations.
Tips for Effectively Using Utility Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
- Regularly update and verify the accuracy of the data.
- Use the map as a communication tool to share information with stakeholders.
- Integrate the map into all planning, construction, and maintenance activities.
- Utilize the map for risk assessment and mitigation.
- Consider using GIS software to enhance the functionality and capabilities of the utility map.
Conclusion: Utility Maps – A Foundation for Efficient and Safe Infrastructure Management
Utility maps are indispensable tools for managing and maintaining the complex network of essential utilities that underpin our modern society. By providing a comprehensive visual representation of infrastructure, they enhance safety, facilitate planning, promote collaboration, and optimize operations. As technology continues to advance, utility maps will play an even more crucial role in ensuring the efficient, reliable, and sustainable delivery of essential services.




![GIS for Electric Utilities [The Ultimate Guide] GIS Cloud](https://www.giscloud.com/assets/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GIS-for-Electric-Utilities-electrical-distribution-planning_1644595051.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Utility Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!