Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Ladoga’s Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Ladoga’s Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Ladoga’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Ladoga’s Geography

Lake Ladoga, the largest lake in Europe, holds a captivating allure for both nature enthusiasts and explorers. Its vast expanse, dotted with islands and shrouded in history, invites a closer look. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Lake Ladoga’s geography, highlighting its unique characteristics and the significance of its intricate map.
A Glimpse into the Heart of Europe’s Largest Lake
Lake Ladoga, situated in the northwestern part of Russia, stretches across a remarkable 17,700 square kilometers (6,830 square miles). Its elongated shape, resembling a gigantic, irregular crescent, is a testament to its formation through glacial activity. The lake’s depth varies considerably, with an average depth of 51 meters (167 feet) and a maximum depth of 230 meters (754 feet). This depth, coupled with its vast surface area, contributes to Lake Ladoga’s significant role in the region’s hydrography and ecosystem.
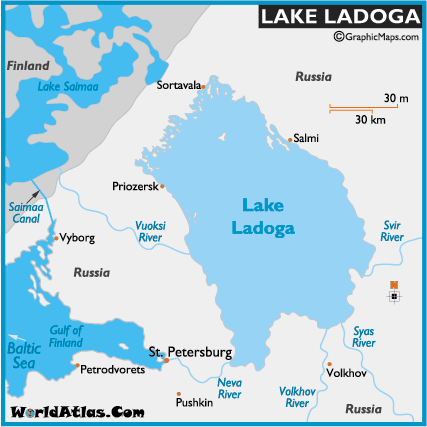
Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding Lake Ladoga’s Map
The map of Lake Ladoga is a complex tapestry of interconnected waterways, islands, and peninsulas. Its intricate layout reflects the lake’s dynamic history and its multifaceted role as a vital transportation route, a haven for diverse wildlife, and a source of economic activity.
Key Features of Lake Ladoga’s Map:
-
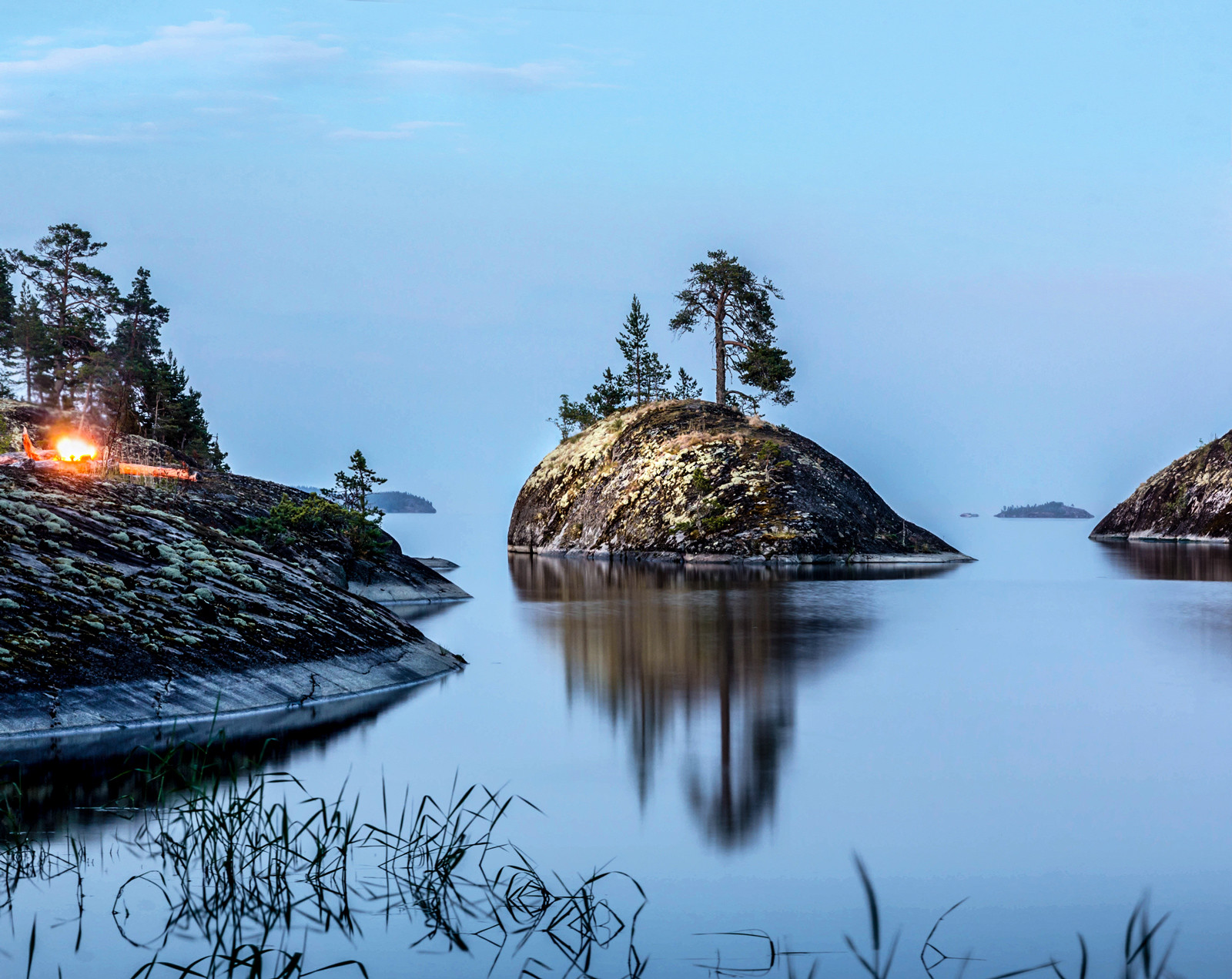
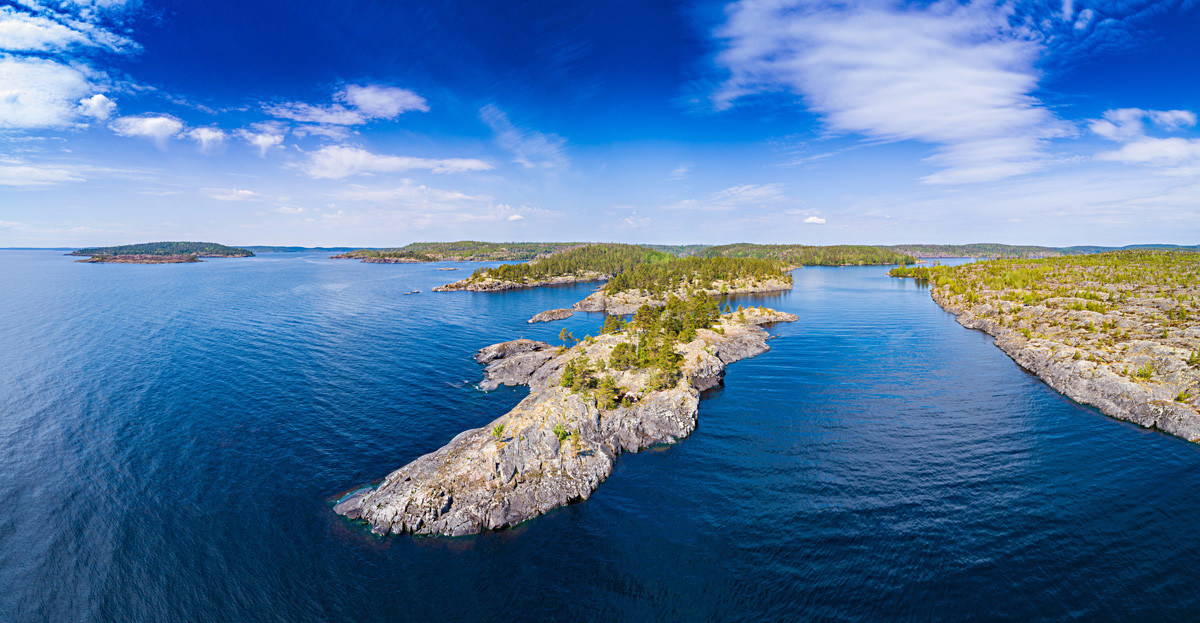
Islands: Lake Ladoga is home to over 660 islands, each with its unique character and history. The largest island, Valaam, is a renowned spiritual center, known for its ancient monasteries and breathtaking natural beauty. Other notable islands include Konevets, known for its monastery and scenic landscapes, and Berezovy, renowned for its rich birdlife.
-
Peninsulas: Several peninsulas jut out into the lake, adding further complexity to its geography. The Svir Peninsula, located in the northern part of the lake, is a significant feature, separating the Svir River from the main body of the lake.
-
Rivers and Channels: Numerous rivers flow into Lake Ladoga, contributing to its water volume and playing a crucial role in its ecosystem. The Neva River, which flows out of the lake, connects it to the Baltic Sea. The Svir River, connecting Lake Onega to Lake Ladoga, is a vital waterway for navigation and transportation.
-
Bays and Gulfs: The lake’s coastline is characterized by numerous bays and gulfs, creating diverse habitats for various species of fish and aquatic life. The largest bay, the Svir Bay, is situated at the northern end of the lake and is known for its shallow waters and rich biodiversity.
Beyond the Surface: Unveiling the Significance of Lake Ladoga’s Map
The map of Lake Ladoga is more than just a geographical representation. It holds significant historical, ecological, and economic value.
-
Historical Significance: The lake has been a crucial waterway for centuries, connecting different regions and facilitating trade. Its shores have witnessed numerous historical events, from Viking raids to the construction of fortresses and the development of settlements. The map reflects these historical layers, offering insights into the region’s past.
-
Ecological Importance: Lake Ladoga is a vital habitat for diverse flora and fauna. Its waters support a rich ecosystem, including numerous species of fish, birds, and mammals. The map provides a framework for understanding the distribution of these species and the interconnectedness of the lake’s ecosystem.
-
Economic Value: The lake plays a significant role in the local economy, supporting fishing, tourism, and transportation industries. The map guides navigation and facilitates access to the lake’s resources, contributing to economic development.
Navigating the Depths: FAQs about Lake Ladoga’s Map
1. What are the main cities and towns located on the shores of Lake Ladoga?
The main cities and towns located on the shores of Lake Ladoga include:
-
St. Petersburg: Located at the western end of the lake, St. Petersburg is a major cultural and economic center of Russia, with a rich history and vibrant cultural scene.
-
Sortavala: Situated on the northern shore of the lake, Sortavala is a charming town known for its picturesque landscapes and its connection to the Karelian Isthmus.
-
Priozersk: Located on the northwestern shore of the lake, Priozersk is a historical town known for its medieval fortress and its proximity to the Valaam archipelago.
-
Novaya Ladoga: Situated on the southern shore of the lake, Novaya Ladoga is a town with a rich history, known for its role in the defense of the region during the Second World War.
2. What are the main islands in Lake Ladoga?
The main islands in Lake Ladoga include:
-
Valaam: The largest island, Valaam is a renowned spiritual center, known for its ancient monasteries and breathtaking natural beauty.
-
Konevets: Located in the northwestern part of the lake, Konevets is known for its monastery, which dates back to the 14th century, and its scenic landscapes.
-
Berezovy: Located in the central part of the lake, Berezovy is known for its rich birdlife and its role as a breeding ground for various species.
-
Rybatsky: Located in the southwestern part of the lake, Rybatsky is known for its historical significance and its role as a fishing center.
3. What are the main rivers that flow into Lake Ladoga?
The main rivers that flow into Lake Ladoga include:
-
Neva River: The main river that flows out of Lake Ladoga, connecting it to the Baltic Sea.
-
Svir River: A vital waterway that connects Lake Onega to Lake Ladoga, facilitating navigation and transportation.
-
Vuoksa River: A river that flows from Finland into Lake Ladoga, contributing to its water volume and biodiversity.
-
Syas River: A river that flows from the north into Lake Ladoga, contributing to its water volume and playing a role in its ecosystem.
4. What are the main types of fish found in Lake Ladoga?
Lake Ladoga is known for its diverse fish population, including:
-
Pike: A predatory fish that is commonly found in the lake’s deeper waters.
-
Perch: A popular sport fish that is found in both shallow and deep waters.
-
Burbot: A bottom-dwelling fish that is found in the lake’s colder waters.
-
Whitefish: A commercially important fish that is found in the lake’s deeper waters.
-
Salmon: A migratory fish that is found in the lake’s tributaries and is a popular target for anglers.
5. What are the main tourist attractions located on the shores of Lake Ladoga?
The shores of Lake Ladoga offer a variety of tourist attractions, including:
-
Valaam Monastery: A renowned spiritual center located on the largest island in the lake, known for its ancient monasteries and breathtaking natural beauty.
-
Konevets Monastery: A historical monastery located on an island in the northwestern part of the lake, known for its scenic landscapes and its connection to the Karelian Isthmus.
-
Priozersk Fortress: A medieval fortress located on the northwestern shore of the lake, known for its historical significance and its role in the defense of the region.
-
Sortavala: A charming town located on the northern shore of the lake, known for its picturesque landscapes and its connection to the Karelian Isthmus.
-
Novaya Ladoga: A town located on the southern shore of the lake, known for its rich history and its role in the defense of the region during the Second World War.
Tips for Exploring Lake Ladoga’s Geography:
-
Utilize a detailed map: A comprehensive map of Lake Ladoga is essential for navigating its intricate waterways and identifying key landmarks.
-
Consider a guided tour: Guided tours offer insights into the lake’s history, ecology, and culture, enhancing the overall experience.
-
Explore the islands: Visiting the islands, particularly Valaam and Konevets, provides a unique perspective on the lake’s natural beauty and cultural heritage.
-
Engage in water activities: Lake Ladoga offers opportunities for fishing, boating, and kayaking, allowing visitors to experience the lake’s vastness and diverse ecosystem.
-
Respect the environment: It is crucial to respect the lake’s ecosystem by avoiding littering, preserving wildlife, and adhering to local regulations.
Conclusion: A Testament to Nature’s Grandeur
Lake Ladoga’s map is a testament to the intricate tapestry of nature, revealing its unique characteristics and the significance of its geography. Its vast expanse, dotted with islands and shrouded in history, invites a deeper understanding of its role in the region’s history, ecology, and economy. By exploring its depths, both literally and figuratively, we gain a profound appreciation for the grandeur of this European treasure.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Lake Ladoga’s Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!