Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns
Related Articles: Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns
- 3.1 Navigating the Landscape of Pollution: A Visual Guide
- 3.2 Delving Deeper: Sources of Pollution
- 3.3 The Human and Environmental Cost of Pollution
- 3.4 Navigating the Path Towards Cleaner Air
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns

California, renowned for its diverse landscapes and thriving economy, faces a persistent challenge: air pollution. Understanding the distribution and sources of this pollution is crucial for enacting effective policies and safeguarding public health. This article delves into the intricacies of air pollution in California, examining its geographical patterns, key sources, and the implications for residents and the environment.
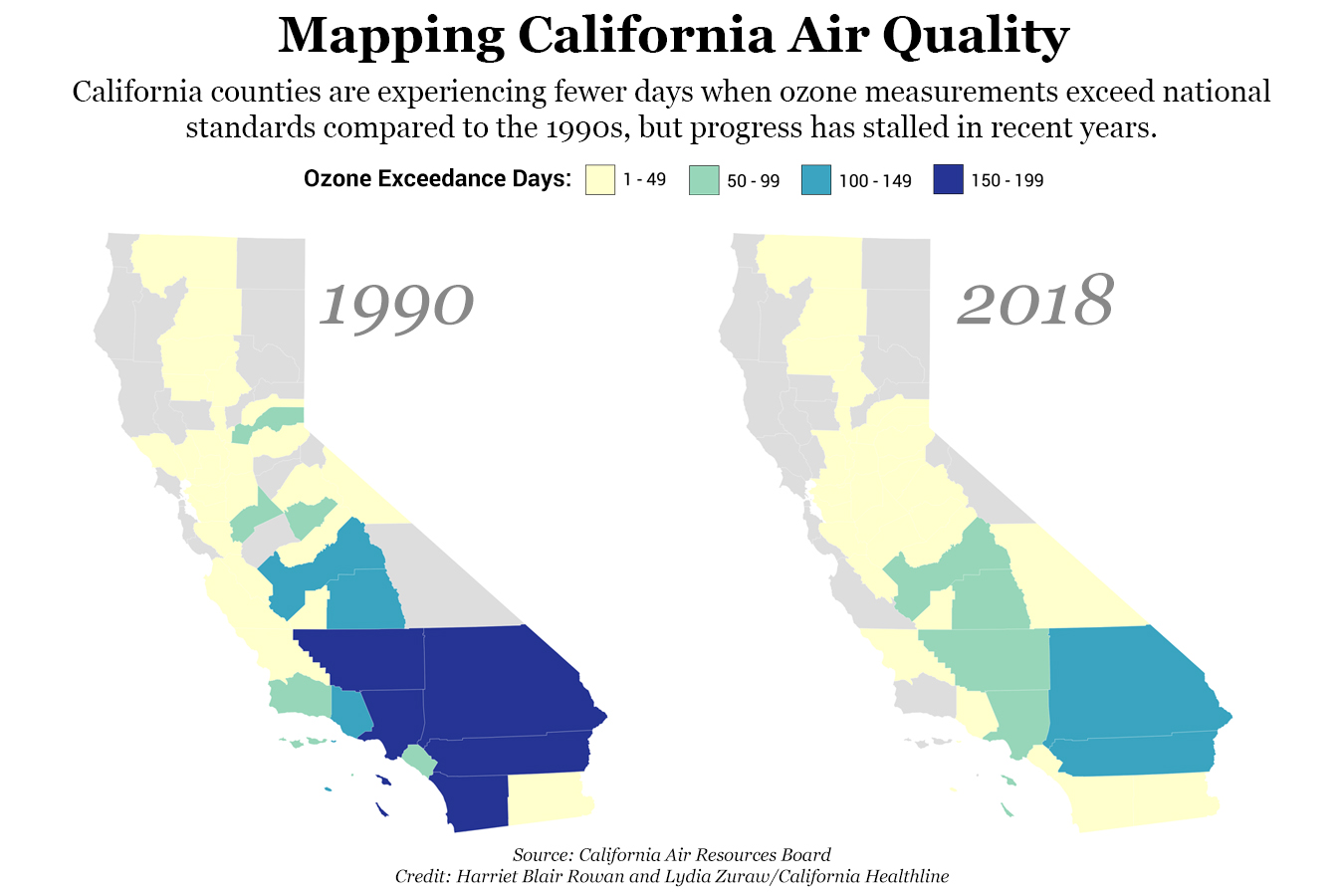
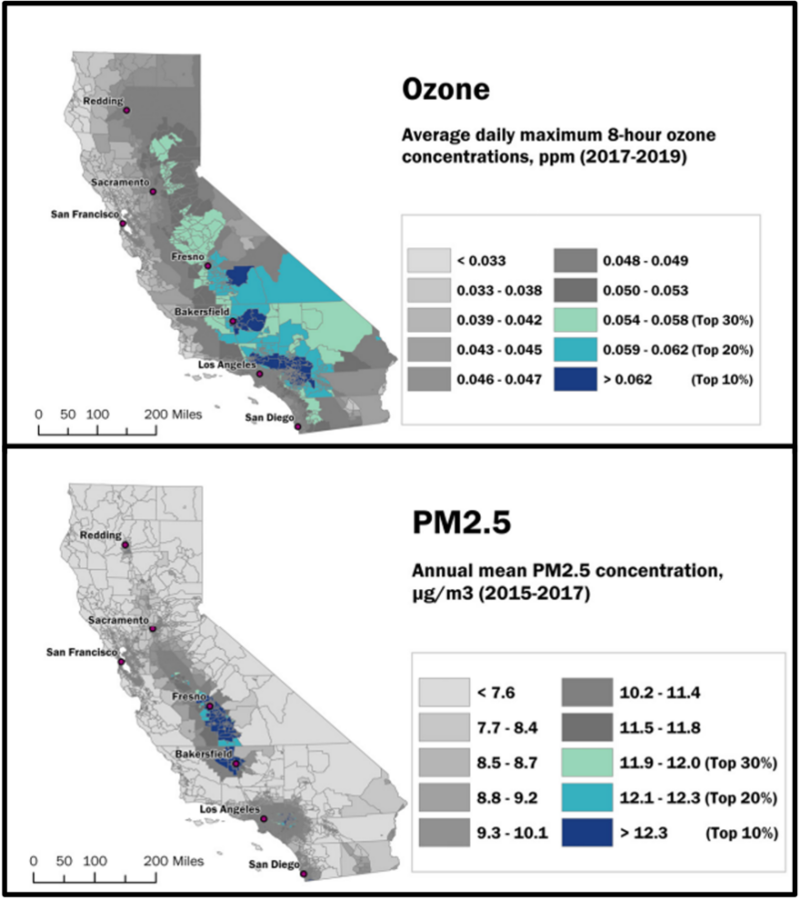
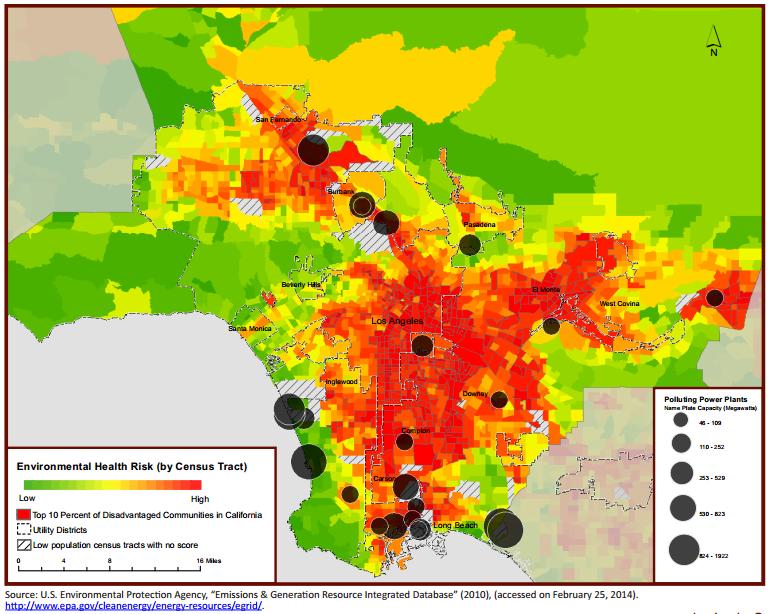
Navigating the Landscape of Pollution: A Visual Guide
Visualizing pollution patterns through maps provides a powerful tool for comprehending the spatial distribution of air quality issues. California’s air pollution map reveals a complex tapestry of hotspots and relatively clean areas, influenced by various factors.
The Major Players:
- Urban Centers: Metropolitan areas like Los Angeles, San Francisco, and San Diego experience higher concentrations of pollutants due to heavy traffic, industrial activity, and dense populations.
- Agricultural Regions: The Central Valley, a major agricultural hub, faces challenges from agricultural emissions, including dust, pesticides, and ammonia.
- Coastal Areas: While generally benefiting from ocean breezes, coastal areas are susceptible to localized pollution from shipping, industrial facilities, and urban sprawl.
- Mountainous Regions: Elevated areas often experience elevated ozone levels due to the interaction of pollutants with sunlight.
Key Pollutants:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These microscopic particles, originating from various sources including vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, and wildfires, pose significant health risks.
- Ozone (O3): Formed through chemical reactions involving nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, ozone is a major component of smog and can damage respiratory systems.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Primarily emitted from vehicle exhaust, carbon monoxide can reduce oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): Released from combustion processes, nitrogen dioxide contributes to smog formation and respiratory problems.
The Importance of Data Visualization:
Air pollution maps serve as a valuable tool for:
- Identifying pollution hotspots: Maps highlight areas with elevated pollution levels, allowing authorities to focus resources and interventions effectively.
- Tracking pollution trends: Comparing maps over time reveals changes in pollution patterns, aiding in understanding the impact of policies and environmental factors.
- Public awareness: Visual representations of air quality data can educate the public about the extent and severity of pollution, promoting awareness and engagement in mitigation efforts.
Delving Deeper: Sources of Pollution
Understanding the sources of air pollution is paramount for developing effective strategies to reduce its impact. California’s diverse geography and economic activities contribute to a complex tapestry of pollution sources:
Transportation:
- Vehicle emissions: California’s extensive road network and reliance on personal vehicles make transportation a significant contributor to air pollution.
- Port activity: Shipping vessels, particularly those operating in busy ports like Los Angeles and Long Beach, release substantial amounts of pollutants.
- Aviation: Air traffic contributes to air pollution, particularly in regions with major airports.
Industry:
- Manufacturing: Industrial processes, including refining, chemical production, and power generation, emit a range of pollutants.
- Agriculture: Agricultural activities, such as fertilizer application, livestock operations, and crop dusting, release pollutants like ammonia and dust.
- Waste management: Waste incineration and landfills contribute to air pollution, particularly with particulate matter and greenhouse gases.
Wildfires:
- Increased frequency and intensity: Climate change is exacerbating wildfire activity, leading to significant smoke plumes that impact air quality across the state.
- Smoke composition: Wildfire smoke contains a complex mixture of pollutants, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds.
Other Sources:
- Construction: Construction activities, including demolition and excavation, release dust and other pollutants.
- Residential sources: Domestic activities like cooking, heating, and lawn care contribute to air pollution, particularly in urban areas.
The Human and Environmental Cost of Pollution
Air pollution has profound consequences for both human health and the environment:
Health Impacts:
- Respiratory problems: Air pollution can trigger asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions.
- Cardiovascular disease: Exposure to particulate matter and ozone can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Cancer: Some air pollutants, such as benzene and formaldehyde, are known carcinogens.
- Cognitive impairment: Studies suggest that prolonged exposure to air pollution can negatively impact cognitive function and brain development.
Environmental Impacts:
- Climate change: Air pollutants like carbon dioxide and methane contribute to global warming and climate change.
- Acid rain: Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water in the atmosphere to form acid rain, which can damage forests, lakes, and buildings.
- Visibility reduction: Air pollution, particularly particulate matter, can reduce visibility, impacting transportation safety and tourism.
- Ecosystem damage: Pollutants can harm sensitive ecosystems, including forests, wetlands, and aquatic habitats.
Navigating the Path Towards Cleaner Air
Addressing California’s air pollution challenge requires a multi-pronged approach:
Policy and Regulation:
- Stricter emission standards: Enacting and enforcing stricter emission standards for vehicles, industries, and other sources of pollution is crucial.
- Clean air regulations: Implementing and enforcing regulations to control air pollution from various sources, including industrial facilities, power plants, and agricultural operations.
- Incentives for cleaner technologies: Providing financial incentives and tax breaks to encourage the adoption of cleaner technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.
Technological Innovation:
- Advanced emission control technologies: Developing and implementing advanced emission control technologies for vehicles, industries, and power plants.
- Renewable energy sources: Increasing the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Electric vehicles: Promoting the adoption of electric vehicles to reduce transportation-related emissions.
Community Engagement:
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about the health and environmental impacts of air pollution and promoting individual actions to reduce emissions.
- Community-based monitoring: Engaging communities in air quality monitoring and data collection to identify local pollution sources and inform policy decisions.
- Sustainable transportation options: Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking to reduce reliance on private vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most polluted area in California?
The Los Angeles Basin, including Los Angeles and surrounding areas, consistently ranks among the most polluted regions in the state, with high levels of ozone, particulate matter, and other pollutants.
2. How does air pollution affect my health?
Air pollution can trigger respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other health issues. Individuals with pre-existing conditions, children, and the elderly are particularly vulnerable.
3. What can I do to reduce my impact on air pollution?
You can reduce your impact by driving less, using public transportation, cycling, or walking; choosing fuel-efficient vehicles; avoiding idling; and using energy-efficient appliances.
4. What are the current air quality regulations in California?
California has stringent air quality regulations, including vehicle emission standards, industrial emission limits, and programs to address agricultural emissions.
5. How is climate change impacting air pollution in California?
Climate change is exacerbating wildfire activity, leading to increased smoke pollution. It is also influencing weather patterns, potentially impacting the formation and distribution of ozone and other pollutants.
Tips for Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution
- Check air quality forecasts: Stay informed about air quality conditions in your area by checking websites like the California Air Resources Board (CARB) or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Reduce outdoor activity on high-pollution days: When air quality is poor, limit outdoor activities, especially strenuous ones.
- Wear a mask: Consider wearing a mask when engaging in outdoor activities on high-pollution days.
- Keep your home clean: Regularly clean your home to reduce dust and other pollutants.
- Support clean air initiatives: Advocate for policies and regulations that promote clean air and reduce pollution.
Conclusion
California’s air pollution map paints a stark picture of the challenges facing the state. Understanding the spatial distribution of pollution, identifying key sources, and acknowledging the human and environmental costs are crucial for enacting effective policies and promoting cleaner air. By implementing a multi-pronged approach involving stricter regulations, technological innovation, and community engagement, California can strive towards a future with improved air quality and a healthier environment for all.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling California’s Air Quality: A Comprehensive Look at Pollution Patterns. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!