Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map
- 3.1 Defining the Meridian Lines: Understanding Longitude
- 3.2 The Importance of Longitude in Geographic Mapping
- 3.3 Exploring the Grid: Key Features of the Longitude Map
- 3.4 The Evolution of Longitude Measurement: From Sextants to Satellites
- 3.5 FAQs about Longitude and the Longitude Map
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding and Using Longitude Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Longitude
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map
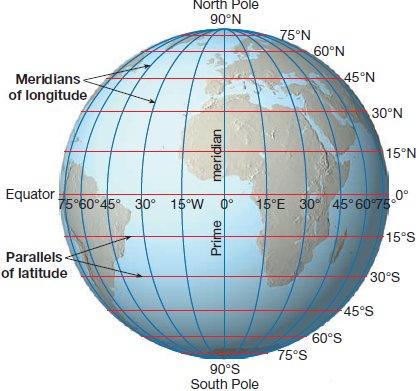
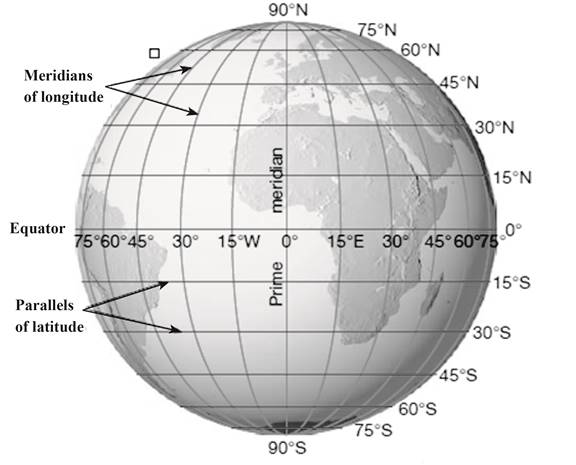
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, presents a challenge when attempting to pinpoint specific locations. Enter the longitude map, a crucial tool for navigation, mapping, and understanding the planet’s geography. This intricate system of lines, running vertically from pole to pole, forms the basis of our understanding of global coordinates and serves as the backbone for countless applications, from air travel to satellite communication.
Defining the Meridian Lines: Understanding Longitude
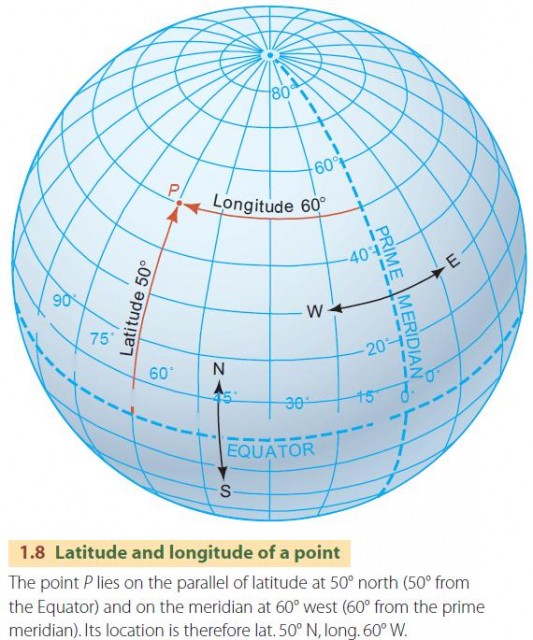
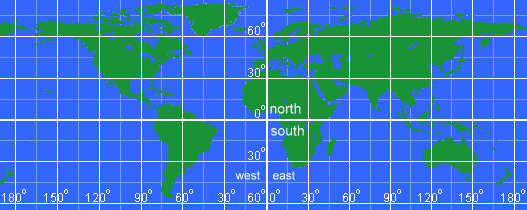
Longitude, often referred to as "meridians," consists of imaginary lines that circle the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole. Each meridian represents a specific angular distance, measured in degrees, east or west of the prime meridian, which serves as the zero-degree reference point. This prime meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, acts as the dividing line between the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
The Importance of Longitude in Geographic Mapping
The significance of longitude lies in its ability to provide a precise location for any point on Earth. Combined with latitude, which measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, longitude forms the foundation of the geographic coordinate system. This system allows for accurate location identification and is essential for various fields:
- Navigation: Sailors, pilots, and travelers rely on longitude to determine their position on the globe and plot courses.
- Mapping: Longitude is indispensable for creating accurate maps, enabling the depiction of continents, countries, cities, and other geographic features in their correct positions.
- Satellite Communication: Satellites use longitude to communicate with ground stations and transmit signals across vast distances.
- Time Zones: The Earth’s rotation and the longitude system define time zones, ensuring consistent timekeeping around the globe.
Exploring the Grid: Key Features of the Longitude Map
The longitude map comprises several key elements:
- Prime Meridian: The zero-degree meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, serves as the reference point for measuring longitude.
- Meridian Lines: These imaginary lines run vertically from pole to pole, each representing a specific angular distance east or west of the prime meridian.
- Degrees of Longitude: Longitude is measured in degrees, with 180 degrees east and 180 degrees west of the prime meridian.
- Minutes and Seconds: Each degree of longitude is further divided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds, providing a highly precise measurement of location.
- International Date Line: Located roughly along the 180th meridian, this imaginary line marks the transition between calendar days.
The Evolution of Longitude Measurement: From Sextants to Satellites
Historically, determining longitude presented a significant challenge. Early navigators relied on celestial observations, using instruments like sextants to measure the angle between celestial bodies and the horizon. However, these methods were prone to errors and required skilled observers.
The invention of the chronometer in the 18th century revolutionized longitude determination. By comparing the time at a known location with the time at the observer’s location, sailors could calculate their longitude with greater accuracy. This breakthrough significantly improved maritime navigation and trade.
Today, with the advent of GPS technology, determining longitude is a simple matter. Global Positioning System satellites continuously transmit signals that enable receivers on Earth to calculate their precise location, including longitude, latitude, and altitude.
FAQs about Longitude and the Longitude Map
1. What is the difference between longitude and latitude?
Longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian, while latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator.
2. Why is the prime meridian located in Greenwich, England?
The prime meridian’s location in Greenwich was established by international agreement in the late 19th century, primarily due to the prominence of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich and the widespread use of the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as a standard time reference.
3. How is longitude used in time zones?
The Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours, and this rotation is reflected in the longitude system. Each 15 degrees of longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in time. This principle forms the basis for time zones, dividing the globe into 24 time zones, each encompassing 15 degrees of longitude.
4. What is the International Date Line, and why is it important?
The International Date Line, roughly following the 180th meridian, marks the transition between calendar days. When crossing the International Date Line eastward, one gains a day, while crossing it westward results in losing a day. This line ensures consistent timekeeping across the globe, preventing confusion with dates and times.
5. How does GPS technology utilize longitude?
GPS receivers on Earth utilize signals from multiple GPS satellites to calculate their precise location. These signals contain information about the satellite’s position, including its longitude, allowing the receiver to determine its own longitude and latitude.
Tips for Understanding and Using Longitude Maps
- Visualize the Grid: Imagine the Earth as a globe with lines running vertically from pole to pole, representing longitude.
- Focus on the Prime Meridian: Remember that the prime meridian serves as the zero-degree reference point for measuring longitude.
- Understand the East-West Direction: Longitude is measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian.
- Consider Time Zones: Remember that each 15 degrees of longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in time.
- Explore Online Resources: Utilize online maps and interactive globes to visualize longitude and its relationship to latitude.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Longitude
The longitude map, with its intricate network of meridians, remains an essential tool for understanding the Earth’s geography and navigating its vast expanse. From guiding ships across oceans to enabling satellite communication, longitude continues to play a vital role in our modern world. As we explore the planet and beyond, the longitude map will continue to serve as a fundamental framework for our understanding of location, time, and the interconnectedness of our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Longitude Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!