Understanding the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
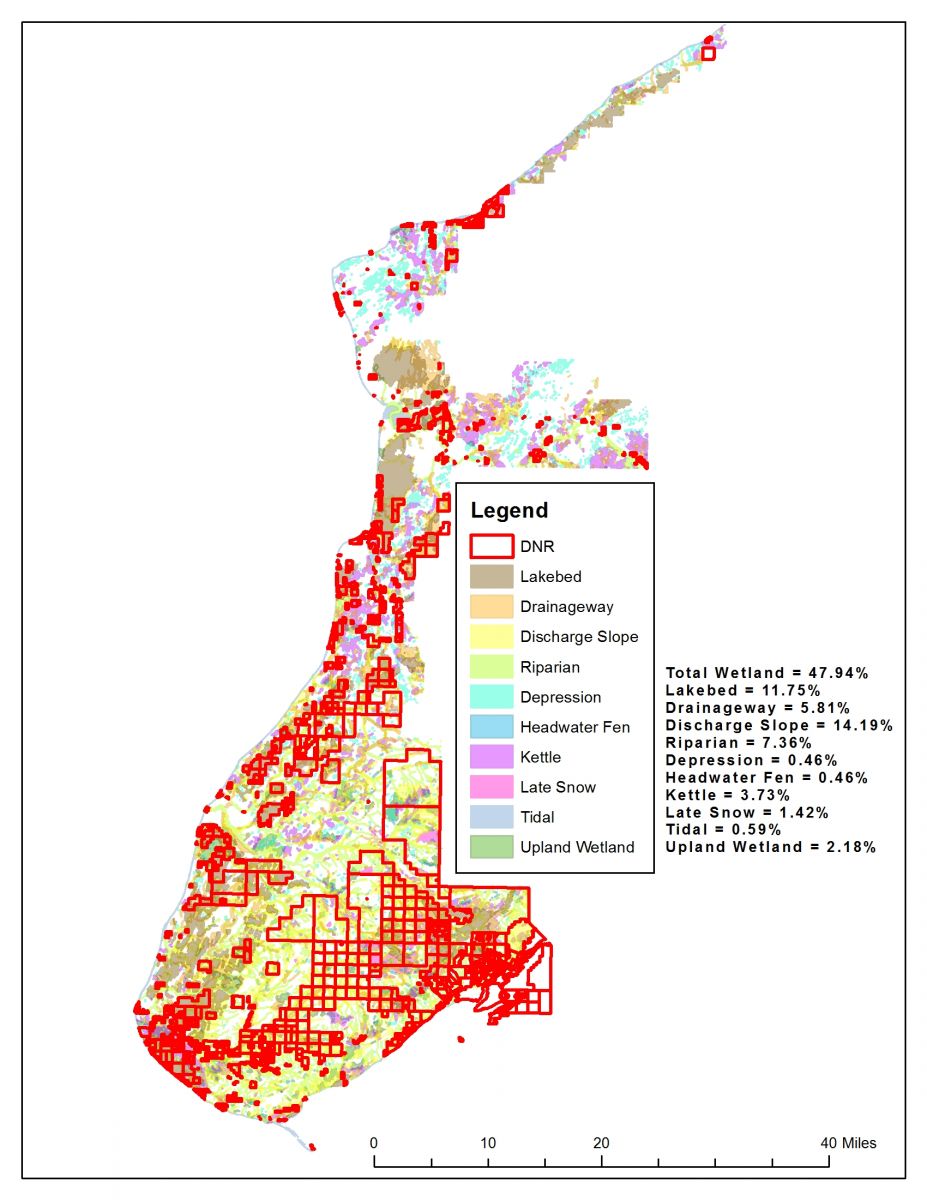
Wetlands, often referred to as "nature’s kidneys," play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. These diverse ecosystems, ranging from marshes and swamps to bogs and fens, provide a multitude of benefits, including water filtration, flood control, and habitat for a wide array of wildlife. Recognizing their significance, many state and federal agencies, including the Department of Natural Resources (DNR), have implemented comprehensive wetland mapping programs.
DNR Wetland Maps: A Window into the Ecosystem
DNR wetland maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the distribution, characteristics, and ecological significance of wetlands within a specific region. These maps are meticulously created using a variety of techniques, including aerial photography, remote sensing, and field surveys. The resulting data is then compiled into a comprehensive map, providing a detailed picture of the wetland landscape.
Benefits of DNR Wetland Maps
The benefits of DNR wetland maps extend far beyond simply visualizing the location of wetlands. They provide crucial information for a wide range of applications, including:
- Conservation and Management: DNR wetland maps are essential for developing effective conservation and management strategies. By identifying the location and condition of wetlands, agencies can prioritize conservation efforts, implement restoration programs, and mitigate potential threats.
- Land Use Planning: These maps are invaluable for land use planning, helping to ensure that development projects are sited appropriately and minimize impacts on wetlands. By understanding the location and ecological value of wetlands, planners can make informed decisions that balance development needs with environmental protection.
- Water Quality Management: Wetlands act as natural filters, removing pollutants from water. DNR wetland maps help to identify areas where wetland restoration or protection is necessary to improve water quality and ensure the health of aquatic ecosystems.
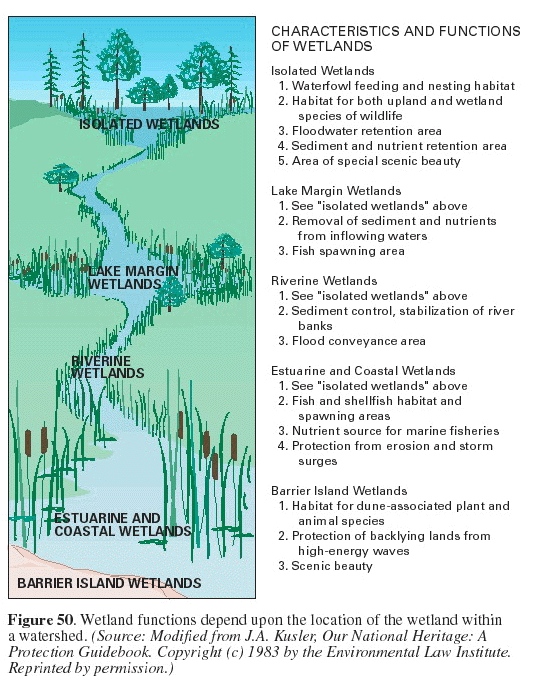
- Wildlife Habitat Management: Wetlands provide critical habitat for a wide variety of wildlife, including birds, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and mammals. DNR wetland maps help to identify areas where wildlife habitat is most abundant, allowing for targeted conservation efforts.
- Flood Control: Wetlands play a vital role in mitigating flood risk by acting as natural sponges, absorbing excess water and slowing down runoff. DNR wetland maps help to identify areas where wetland restoration or protection can enhance flood control capabilities.
- Education and Outreach: These maps are valuable tools for educating the public about the importance of wetlands and promoting awareness of their role in maintaining ecological balance.
Accessing DNR Wetland Maps
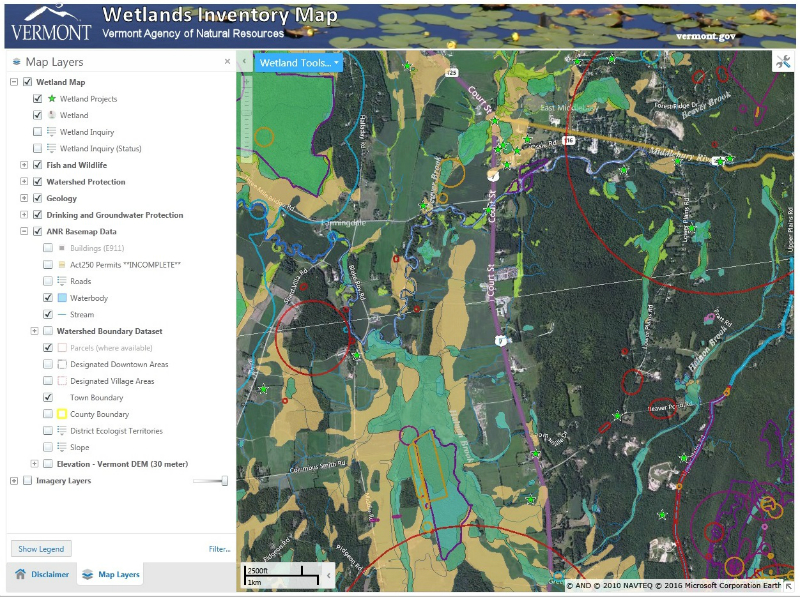
DNR wetland maps are typically available through the agency’s website or through local offices. These maps are often presented in various formats, including online interactive maps, downloadable PDF files, and printed maps. The specific format and accessibility may vary depending on the state and agency.
Interpreting DNR Wetland Maps
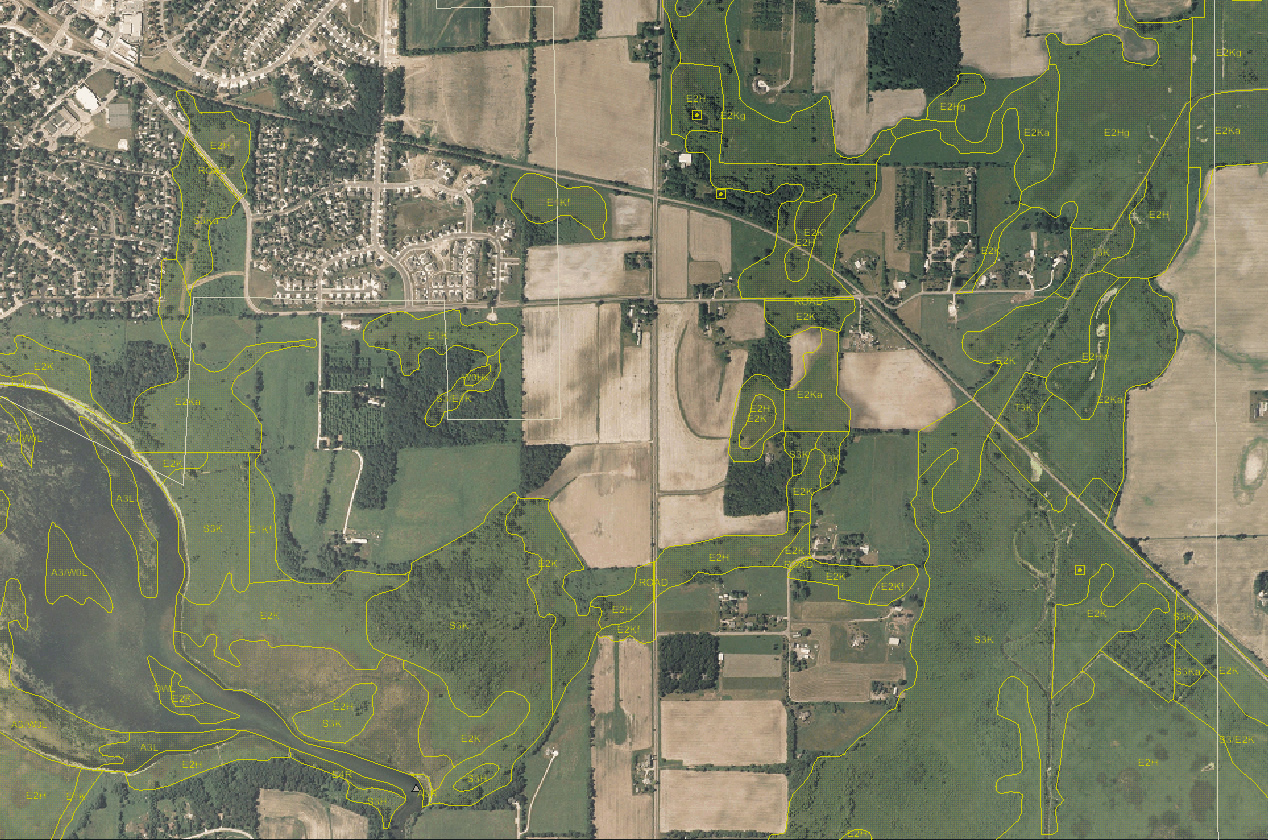
DNR wetland maps are often color-coded to represent different types of wetlands, based on factors such as vegetation, hydrology, and soil type. These maps may also include information on the size, shape, and connectivity of wetlands, as well as any potential threats or stressors.
Understanding Wetland Classifications
DNR wetland maps often employ a classification system to categorize wetlands based on their characteristics. Common wetland classification systems include:
- Cowardin System: This widely used system categorizes wetlands based on vegetation, hydrology, and soil characteristics.
- National Wetlands Inventory (NWI): This system uses aerial photographs and other data to identify and map wetlands across the United States.
- State-Specific Classifications: Many states have developed their own wetland classification systems, often based on local ecological conditions.
FAQs Regarding DNR Wetland Maps
Q: What is the purpose of DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps serve as vital tools for understanding the distribution, characteristics, and ecological significance of wetlands within a specific region. They are used for conservation, management, land use planning, water quality management, wildlife habitat management, flood control, and education.
Q: How are DNR wetland maps created?
A: DNR wetland maps are created using a combination of methods, including aerial photography, remote sensing, and field surveys. The data collected is then compiled into a comprehensive map.
Q: How can I access DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps are typically available through the agency’s website or local offices. They may be presented in various formats, including online interactive maps, downloadable PDF files, and printed maps.
Q: What information is included on DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps typically include information on the location, size, shape, type, and condition of wetlands. They may also indicate potential threats or stressors.
Q: How can I use DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps can be used for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Identifying wetlands for conservation and restoration projects.
- Planning land use to minimize impacts on wetlands.
- Assessing the health and function of wetlands.
- Educating the public about the importance of wetlands.
Tips for Using DNR Wetland Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the map legend: Understanding the symbols, colors, and abbreviations used on the map is crucial for interpreting the information accurately.
- Consider the scale of the map: The scale of the map will determine the level of detail provided. A large-scale map will show more features and information than a small-scale map.
- Use the map in conjunction with other data sources: Combining DNR wetland maps with other data sources, such as soil surveys, aerial photographs, and field observations, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the wetland ecosystem.
- Consult with experts: If you have questions about interpreting the map or using it for specific applications, consult with DNR staff or other wetland experts.
Conclusion
DNR wetland maps are essential resources for understanding and managing these valuable ecosystems. By providing detailed information on the location, characteristics, and ecological significance of wetlands, these maps empower agencies, landowners, and the public to make informed decisions that promote conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of these vital resources. By utilizing DNR wetland maps, we can ensure the continued health and well-being of wetlands, benefiting both present and future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!