Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions
Related Articles: Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions
- 3.1 What are COVID-19 Zoning Maps?
- 3.2 The Importance of COVID-19 Zoning Maps
- 3.3 How to Interpret a COVID-19 Zoning Map
- 3.4 FAQs about COVID-19 Zoning Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using COVID-19 Zoning Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions

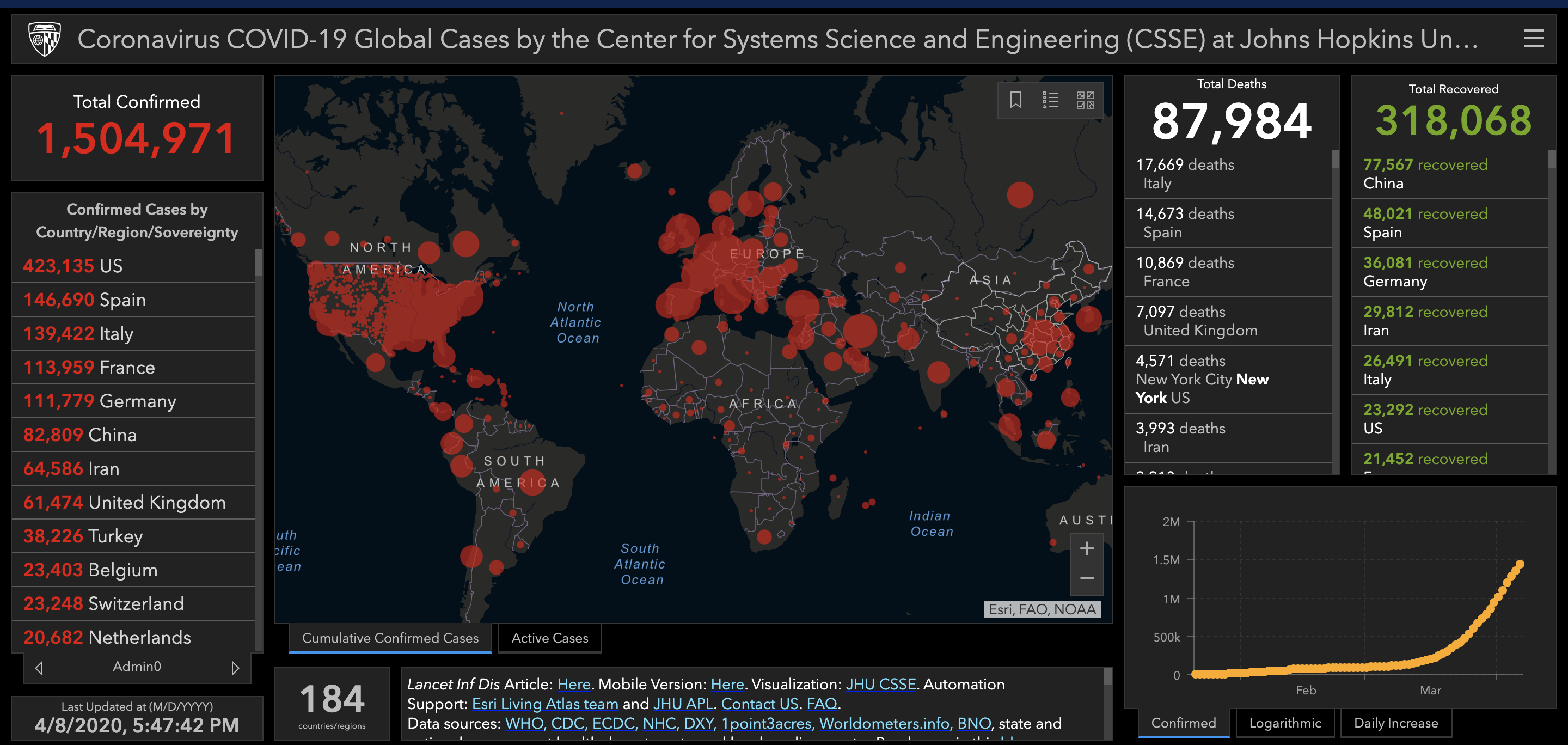
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted our lives, necessitating various public health measures to curb the spread of the virus. One crucial tool employed by authorities to manage the pandemic is the COVID-19 zoning map. These maps, often color-coded, visually represent the geographic distribution of infection rates within a region, providing valuable insights into the pandemic’s trajectory and informing public health decisions.
What are COVID-19 Zoning Maps?
COVID-19 zoning maps, also known as risk maps, are visual representations of the severity of the pandemic within a specific geographic area. They typically depict zones or regions categorized based on key indicators like:
- Case incidence: The number of new COVID-19 cases per unit of population over a defined period.
- Positivity rate: The percentage of COVID-19 tests that come back positive.
- Hospitalization rates: The number of COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals.
- Vaccination rates: The percentage of the population that has received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
These indicators are often combined to create a composite score, which determines the overall risk level of each zone. Zones are typically color-coded, with red indicating high risk, yellow indicating moderate risk, and green indicating low risk.
The Importance of COVID-19 Zoning Maps
COVID-19 zoning maps play a critical role in pandemic management by:
1. Providing Real-Time Data and Insights: Zoning maps offer a clear and concise overview of the pandemic’s spread, allowing authorities to identify areas of concern and target resources effectively.
2. Guiding Public Health Policies: The data displayed on zoning maps informs the implementation of public health measures, such as:
- Social distancing restrictions: Zones with high case numbers may necessitate stricter social distancing guidelines.
- Mask mandates: Zones with elevated risk levels may require mandatory mask-wearing in public spaces.
- Travel restrictions: Zones with high infection rates may be subject to travel restrictions to prevent further spread.
- Testing and vaccination campaigns: Zones with low vaccination rates may require targeted outreach programs to increase vaccination uptake.
3. Empowering Individuals: Zoning maps provide individuals with valuable information about the pandemic’s severity in their local area, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding their personal health and safety.
4. Promoting Transparency and Accountability: Openly accessible zoning maps foster transparency, allowing the public to monitor the pandemic’s progress and hold authorities accountable for their response.
How to Interpret a COVID-19 Zoning Map
Interpreting a zoning map is relatively straightforward. The key is to understand the color coding system and the indicators used to determine the risk level of each zone.
1. Color Coding: The color-coding system typically employs a spectrum from green (low risk) to red (high risk), with yellow representing moderate risk.
2. Indicator Definitions: The map should clearly define the indicators used to determine the risk level of each zone, such as case incidence, positivity rate, hospitalization rates, and vaccination rates.
3. Data Timeframe: The map should specify the timeframe for the data displayed, indicating the period over which the indicators were measured.
4. Geographic Boundaries: The map should clearly define the geographic boundaries of each zone, ensuring accurate identification of the areas with varying levels of risk.
5. Data Sources: The map should cite the sources of the data used, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the information presented.
FAQs about COVID-19 Zoning Maps
1. What are the benefits of using a COVID-19 zoning map?
Zoning maps provide a clear visual representation of the pandemic’s spread, allowing authorities to target resources and implement effective public health measures. They also empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and safety.
2. How frequently are zoning maps updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the region and the availability of data. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated weekly or monthly.
3. What happens if my area is in a high-risk zone?
If your area is in a high-risk zone, it is essential to follow the public health guidelines in place, such as wearing masks, maintaining social distancing, and getting vaccinated.
4. What if I live in a low-risk zone?
Even in low-risk zones, it is crucial to remain vigilant and follow public health recommendations to prevent the spread of the virus.
5. How can I find the zoning map for my area?
Zoning maps are typically available on the websites of local or regional health authorities. You can also find them through news outlets and public health organizations.
Tips for Using COVID-19 Zoning Maps
1. Consult Multiple Sources: Do not rely solely on one zoning map. Compare data from different sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of the pandemic’s spread.
2. Consider Local Context: Zoning maps should be interpreted in conjunction with local context, such as population density, healthcare infrastructure, and social behavior.
3. Stay Informed: Regularly check for updates to zoning maps, as the pandemic situation can change rapidly.
4. Engage in Public Health Measures: Even in low-risk zones, it is essential to practice public health measures like mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination to protect yourself and others.
5. Share Information: Encourage others to use zoning maps and stay informed about the pandemic’s spread.
Conclusion
COVID-19 zoning maps are essential tools for managing the pandemic, providing valuable insights into the virus’s spread and informing public health decisions. By understanding the data displayed on these maps and following public health guidelines, individuals and authorities can work together to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and protect public health. As the pandemic evolves, it is crucial to remain informed, adapt to changing circumstances, and continue to use these maps as a guide for navigating the challenges posed by COVID-19.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding COVID-19 Zoning Maps: A Guide to Navigating Pandemic Restrictions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!