The Triangular Trade: A Network of Exploitation and Exchange
Related Articles: The Triangular Trade: A Network of Exploitation and Exchange
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Triangular Trade: A Network of Exploitation and Exchange. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Triangular Trade: A Network of Exploitation and Exchange

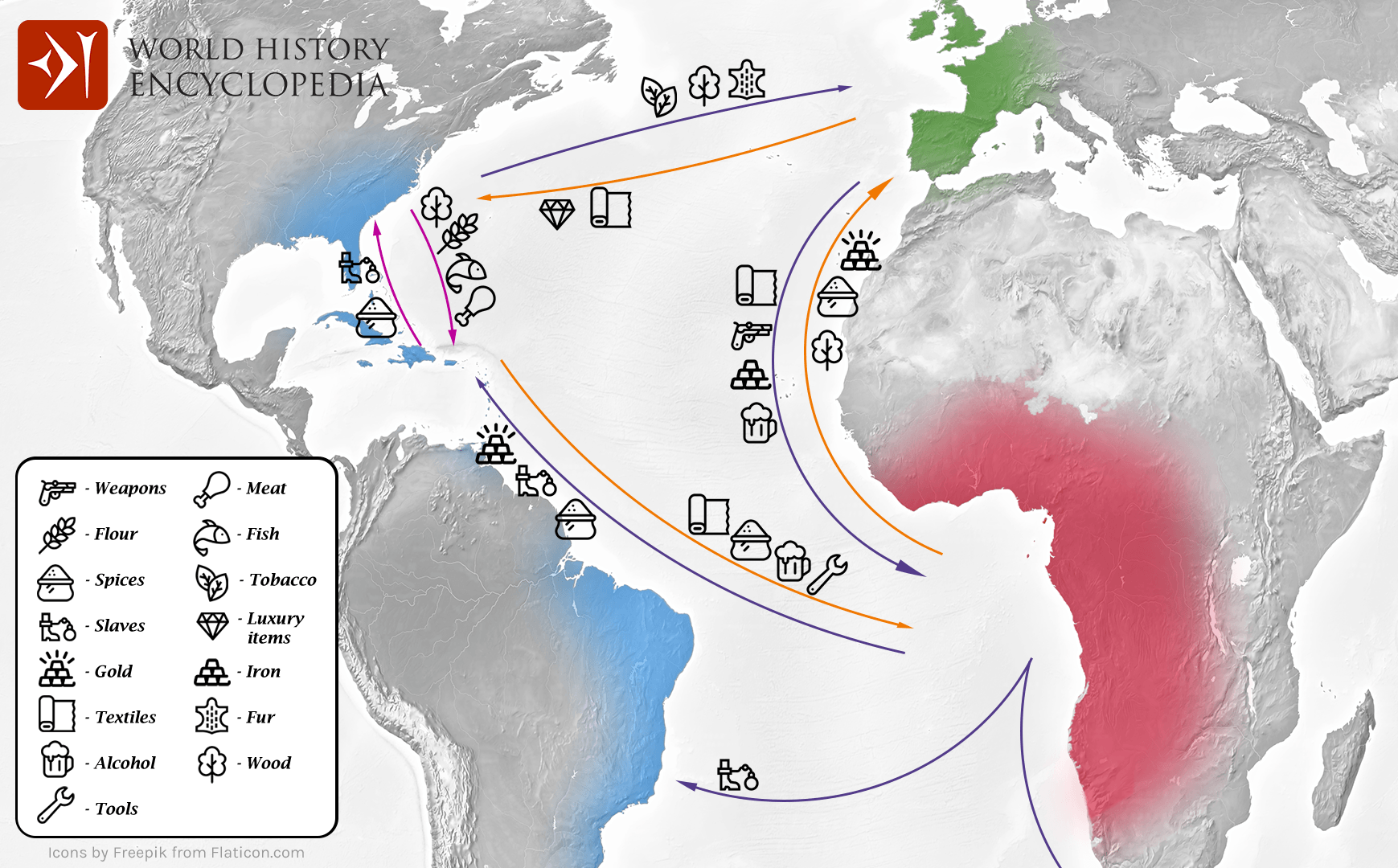
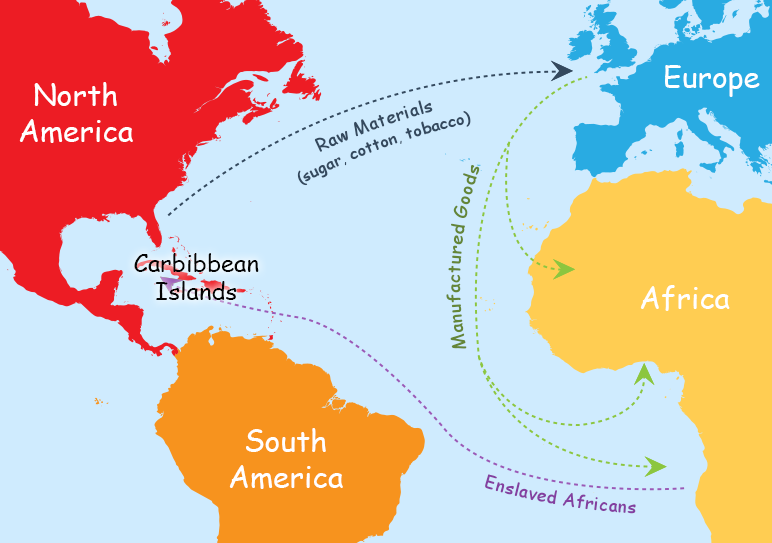
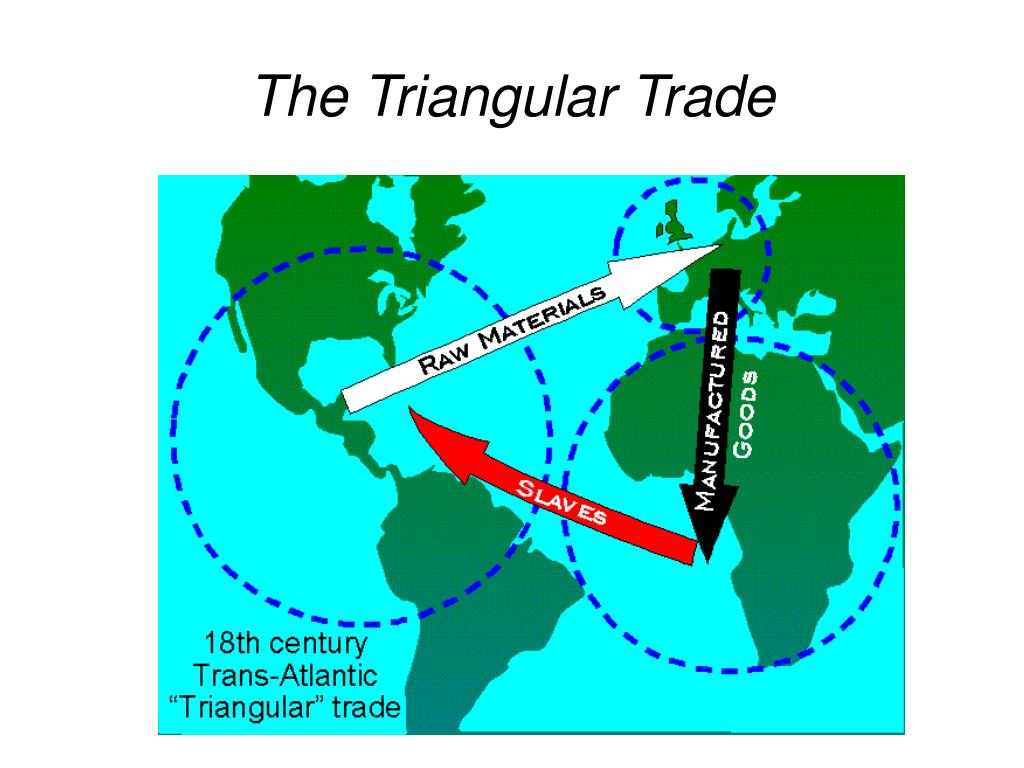
The Triangular Trade, a complex network of transatlantic voyages that dominated global trade from the 16th to the 19th centuries, stands as a stark reminder of the brutal realities of colonialism and the interconnectedness of the world’s economies. This intricate system involved three distinct legs, each carrying a specific cargo and contributing to a cycle of exploitation that profoundly impacted the lives of millions.
Leg 1: The Middle Passage
The first leg of the Triangular Trade, known as the Middle Passage, is the most infamous and tragic. It involved the forced transportation of enslaved Africans from the west coast of Africa to the Americas. This brutal journey, lasting between six and twelve weeks, packed enslaved Africans into cramped and unsanitary ships with minimal food and water. Disease, starvation, and violence were rampant, resulting in a staggering mortality rate of up to 20%.
The enslaved Africans were transported to various destinations in the Americas, primarily the Caribbean, North America, and South America, where they were sold into forced labor on plantations, mines, and other industries. This leg of the trade fueled the demand for cheap labor in the Americas, contributing to the growth of colonial economies and the rise of powerful empires.
Leg 2: The Americas to Europe
The second leg of the Triangular Trade transported raw materials and agricultural products from the Americas to Europe. This leg carried a wide range of commodities, including sugar, tobacco, cotton, coffee, timber, and precious metals. These goods were highly sought after in Europe, where they fueled industrial growth and consumer demand.
The Americas, under European colonial control, became vast producers of these commodities, driven by the forced labor of enslaved Africans. This leg of the trade exemplified the economic exploitation of the Americas by European powers, enriching European nations while contributing to the impoverishment and oppression of indigenous populations.
Leg 3: Europe to Africa
The final leg of the Triangular Trade involved the transportation of manufactured goods from Europe to Africa. These goods included textiles, firearms, alcohol, and other manufactured items that were exchanged for enslaved Africans. This leg of the trade was crucial for sustaining the entire system, providing the necessary resources for the capture and trade of enslaved people.
The exchange of manufactured goods for enslaved Africans created a cycle of dependency and exploitation. It fueled the demand for enslaved labor in the Americas, further perpetuating the cycle of violence and oppression. This leg of the trade also contributed to the destabilization of African societies, undermining local economies and fostering intertribal conflicts.
Beyond the Triangle: A Complex Network
While the Triangular Trade is often depicted as a simple three-part system, it was in reality a far more complex network of trade routes, involving multiple countries and a vast array of goods. The trade routes were not always triangular, with some voyages directly connecting Africa to the Americas or Europe to the Americas.
The Triangular Trade also encompassed various other goods, including spices, tea, porcelain, and ivory. These goods were traded along different routes, adding further complexity to the overall system.
The Legacy of the Triangular Trade
The Triangular Trade left an enduring legacy on the world, shaping the economies, cultures, and social structures of nations across the globe. Its impact is felt today in the demographics, politics, and cultural identities of many countries.
The legacy of the Triangular Trade includes:
- The Transatlantic Slave Trade: The most enduring legacy of the Triangular Trade is the transatlantic slave trade, which resulted in the forced migration of millions of Africans to the Americas. This trade had a profound impact on the demographics of the Americas, contributing to the development of racialized societies and the enduring legacies of slavery and racism.
- Economic Development: The Triangular Trade played a crucial role in the economic development of Europe, contributing to the growth of industrialization and the rise of global capitalism. However, this economic growth came at the expense of the exploitation of enslaved Africans and the plunder of resources from the Americas.
- Cultural Exchange: The Triangular Trade facilitated cultural exchange between different parts of the world. This exchange included the introduction of new crops, foods, music, languages, and religious beliefs. However, this cultural exchange was often accompanied by the imposition of European culture and the suppression of indigenous cultures.
- Political Power: The Triangular Trade played a significant role in the rise of European empires, providing them with the economic resources and military power to expand their influence across the globe. This expansion came at the cost of the subjugation and oppression of indigenous populations and the enslavement of millions of Africans.
The Triangular Trade: A Moral Imperative to Remember
The Triangular Trade stands as a stark reminder of the horrors of colonialism, slavery, and exploitation. Understanding its history and legacy is crucial for recognizing the interconnectedness of the world and the importance of addressing the enduring legacies of colonialism and racism.
FAQs
Q: What was the primary motivation for the Triangular Trade?
A: The primary motivation for the Triangular Trade was profit. European nations sought to exploit the resources of the Americas and the labor of enslaved Africans to generate wealth and power.
Q: How did the Triangular Trade contribute to the development of European economies?
A: The Triangular Trade provided European nations with access to a wide range of raw materials and agricultural products from the Americas, which fueled industrial growth and consumer demand. The trade also generated significant profits for European merchants and investors.
Q: What were the consequences of the Triangular Trade for Africa?
A: The Triangular Trade had devastating consequences for Africa, leading to the enslavement of millions of people, the disruption of local economies, and the destabilization of societies. The trade also contributed to the spread of disease and the introduction of new weapons, which further destabilized the continent.
Q: What were the consequences of the Triangular Trade for the Americas?
A: The Triangular Trade had a profound impact on the Americas, contributing to the development of plantation economies, the growth of cities, and the establishment of racialized societies. However, this development came at the cost of the enslavement of millions of Africans and the oppression of indigenous populations.
Q: How did the Triangular Trade end?
A: The Triangular Trade gradually declined in the 19th century due to a combination of factors, including the rise of abolitionist movements, the increasing cost of slave labor, and the development of new technologies that reduced the need for manual labor. The trade was officially abolished in the 1800s, but its legacy continues to shape the world today.
Tips
- Use primary sources: To gain a deeper understanding of the Triangular Trade, it is essential to consult primary sources, such as diaries, letters, and ship logs. These sources provide firsthand accounts of the experiences of those involved in the trade.
- Explore different perspectives: It is important to consider the perspectives of all those involved in the Triangular Trade, including the enslaved Africans, the European merchants, and the colonial officials. This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities of the trade.
- Connect the past to the present: The Triangular Trade has had a lasting impact on the world, shaping the economies, cultures, and social structures of many nations. It is important to connect the past to the present and to understand how the legacies of the trade continue to shape our world today.
Conclusion
The Triangular Trade, a complex network of transatlantic voyages, stands as a stark reminder of the brutal realities of colonialism and the interconnectedness of the world’s economies. This system of exploitation and exchange, driven by the insatiable greed for profit, had devastating consequences for millions of people, shaping the course of history and leaving an enduring legacy on the world. Understanding its history and legacy is crucial for recognizing the interconnectedness of the world and the importance of addressing the enduring legacies of colonialism and racism. It serves as a powerful reminder of the need for social justice and the importance of recognizing the humanity of all people, regardless of their race, ethnicity, or origin.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Triangular-Trade-58ed395f3df78cd3fce8d0aa.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Triangular Trade: A Network of Exploitation and Exchange. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!