The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology
Related Articles: The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology
- 3.1 The Threat of Feral Hogs: A Multifaceted Issue
- 3.2 Tracking the Spread: Mapping the Feral Hog Presence in Ohio
- 3.3 Factors Contributing to the Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio
- 3.4 Management and Mitigation Efforts: A Multi-pronged Approach
- 3.5 FAQs about Feral Hogs in Ohio:
- 3.6 Tips for Preventing the Spread of Feral Hogs:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology

The presence of feral hogs in Ohio, a state historically considered outside their natural range, has become a pressing concern. While not yet widespread, their documented presence and rapid spread pose a significant threat to Ohio’s agricultural industry, natural ecosystems, and human safety. This article explores the current state of feral hog populations in Ohio, outlining their impact, the factors contributing to their spread, and the ongoing efforts to manage and mitigate their presence.
The Threat of Feral Hogs: A Multifaceted Issue
Feral hogs, also known as wild pigs, are highly adaptable and prolific breeders. They are considered an invasive species, capable of wreaking havoc on diverse environments. In Ohio, their presence carries a range of negative consequences:
1. Agricultural Damage: Feral hogs are notorious for their destructive feeding habits. They root up fields, damaging crops like corn, soybeans, and wheat, causing significant economic losses for farmers. Their rooting behavior also disrupts soil structure, leading to erosion and decreased fertility.
2. Ecological Disruption: Feral hogs are omnivores with a wide diet, consuming a variety of plants, insects, and small animals. Their voracious appetites can disrupt delicate ecological balances, impacting native species and potentially leading to the decline of vulnerable populations.
3. Disease Transmission: Feral hogs are known to carry and transmit various diseases, some of which can affect humans and livestock. These include swine brucellosis, pseudorabies, and leptospirosis, posing a threat to public health and animal welfare.
4. Property Damage: Beyond agricultural fields, feral hogs can damage infrastructure, including fences, roads, and drainage systems. Their rooting behavior can also create hazardous conditions, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
5. Human Safety: Feral hogs can be aggressive, particularly when defending their young or territory. While encounters with humans are relatively infrequent, they can be dangerous, leading to injuries in some cases.
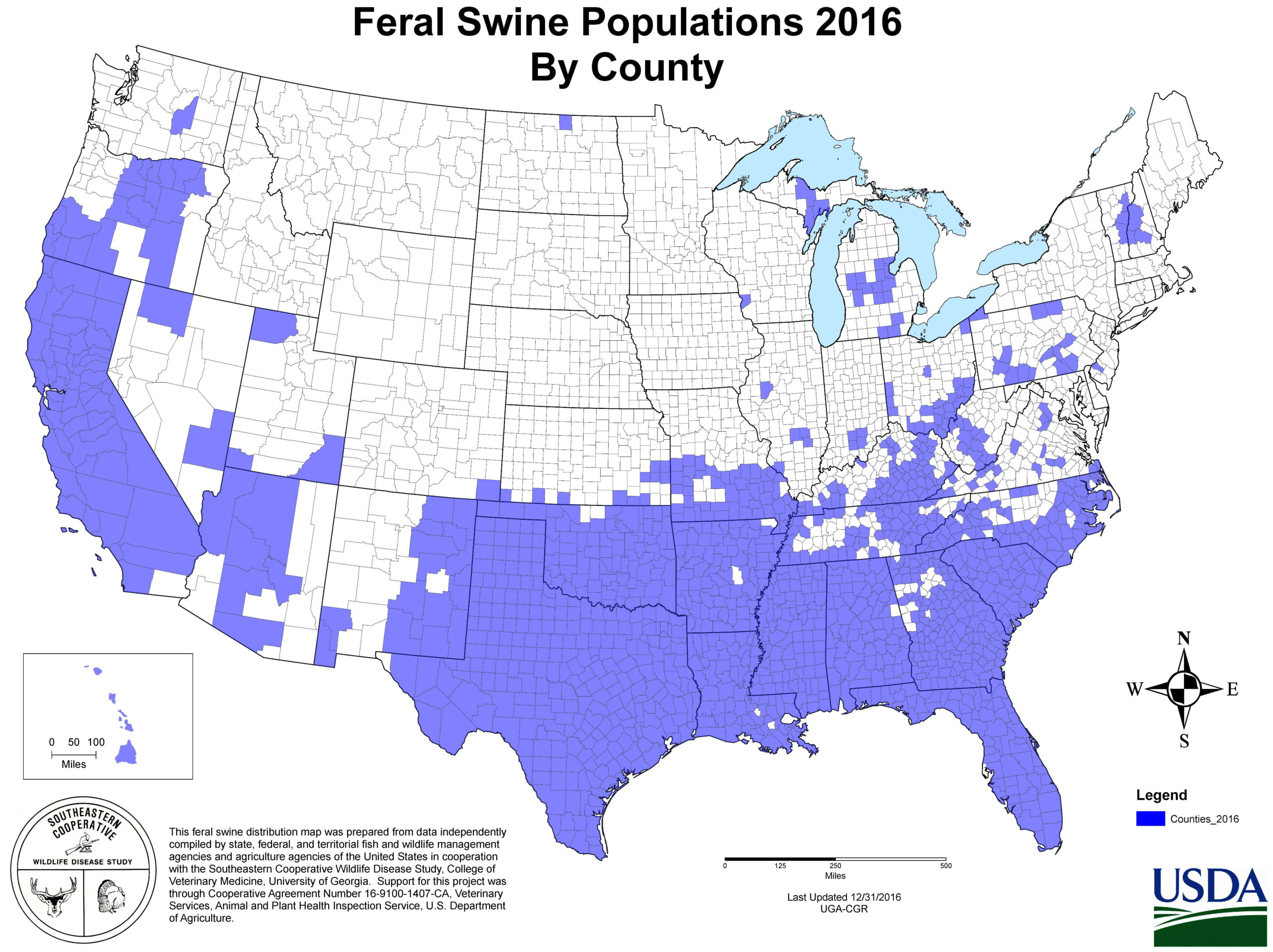
Tracking the Spread: Mapping the Feral Hog Presence in Ohio
The Ohio Department of Natural Resources (ODNR) actively monitors and tracks the spread of feral hogs within the state. While precise population estimates are difficult to obtain, the ODNR maintains a map that records confirmed sightings and reports of feral hog activity. This data is essential for understanding the spatial distribution of feral hogs and guiding management strategies.
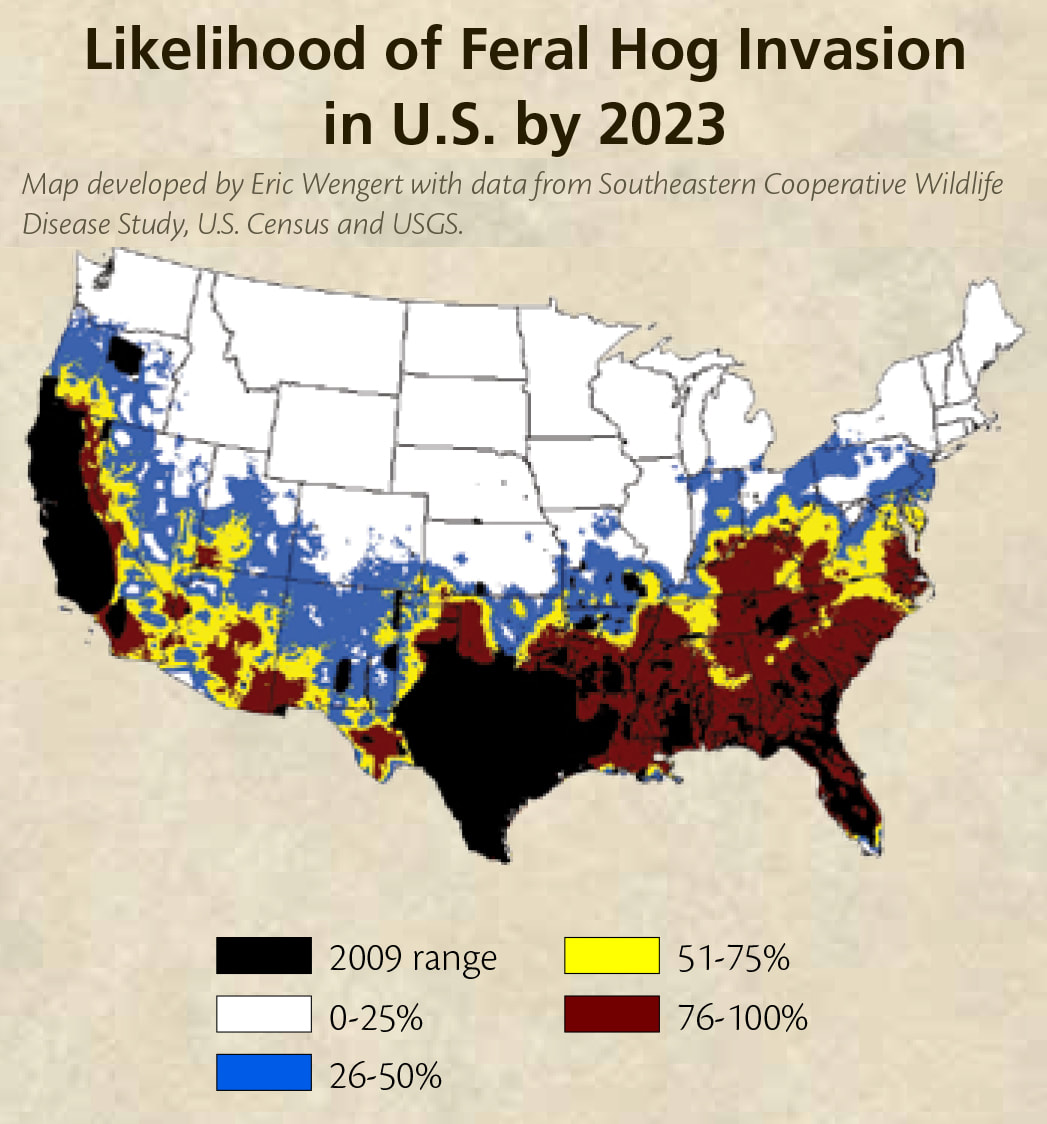
The map reveals a growing presence of feral hogs in Ohio, primarily concentrated in the southern and southeastern regions of the state. This suggests that the animals are likely spreading from neighboring states where they are more established, particularly Kentucky, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. The presence of feral hogs in Ohio is a relatively recent phenomenon, with the first confirmed sightings occurring in the early 2000s. However, their numbers and geographic range have expanded rapidly in recent years, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.
Factors Contributing to the Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio
Several factors contribute to the spread of feral hogs in Ohio:
1. Intentional Releases: Some individuals, often with the intention of establishing hunting opportunities, have illegally released feral hogs into the wild. These introductions have played a significant role in establishing new populations and accelerating their spread.
2. Natural Dispersal: Feral hogs are highly mobile and capable of traversing long distances. They can move naturally into new areas through migration, driven by factors like food availability and breeding opportunities.
3. Human-Assisted Movement: Human activities, such as the transportation of livestock or agricultural products, can inadvertently contribute to the spread of feral hogs. These activities may unintentionally introduce feral hogs into new areas, facilitating their establishment.
4. Lack of Natural Predators: In Ohio, feral hogs lack natural predators capable of effectively controlling their populations. This absence of natural regulation allows their numbers to increase unchecked, leading to rapid population growth and range expansion.
5. Adaptability and Reproductive Capacity: Feral hogs are highly adaptable animals, capable of thriving in a variety of habitats. Their rapid breeding rate, producing multiple litters per year, further contributes to their ability to quickly establish and expand their populations.
Management and Mitigation Efforts: A Multi-pronged Approach
Addressing the threat of feral hogs in Ohio requires a comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies:
1. Public Awareness and Reporting: Educating the public about the threats posed by feral hogs and encouraging the reporting of sightings is crucial for early detection and response. This information allows wildlife officials to track their spread and implement targeted management efforts.
2. Trapping and Removal: Trapping is a common method for controlling feral hog populations. Trapping programs aim to capture and remove individual animals, reducing their numbers and preventing further spread.
3. Hunting and Control Efforts: In some areas, hunting is permitted as a means of controlling feral hog populations. While hunting can be effective, it requires careful management to avoid unintended consequences and ensure the safety of other wildlife.
4. Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government agencies, private landowners, and agricultural organizations is essential for effective feral hog management. Partnerships can leverage resources, expertise, and support to implement comprehensive control programs.
5. Research and Monitoring: Continued research on feral hog behavior, ecology, and control methods is vital for developing effective management strategies. Monitoring population trends and assessing the effectiveness of control measures are crucial for adapting and refining management programs.
FAQs about Feral Hogs in Ohio:
Q: Are feral hogs dangerous to humans?
A: While feral hogs are generally not aggressive towards humans, they can be dangerous if threatened or cornered. They are known to charge and bite, potentially causing serious injuries.
Q: How do I report a feral hog sighting?
A: You can report feral hog sightings to the Ohio Department of Natural Resources (ODNR) through their website or by calling their Wildlife Division.
Q: Can I hunt feral hogs in Ohio?
A: Hunting of feral hogs is permitted in Ohio, but regulations vary by county. Check with the ODNR for specific hunting regulations in your area.
Q: What should I do if I encounter a feral hog?
A: If you encounter a feral hog, do not approach it. Maintain a safe distance and report the sighting to the ODNR.
Tips for Preventing the Spread of Feral Hogs:
1. Secure Food Sources: Store food and garbage securely to prevent attracting feral hogs.
2. Maintain Fencing: Ensure fences are in good condition and adequately secure to prevent feral hogs from entering your property.
3. Report Suspicious Activity: Report any suspicious activity related to feral hogs, such as illegal releases or transportation.
4. Stay Informed: Stay informed about feral hog activity in your area and follow the recommendations of wildlife officials.
Conclusion:
The presence of feral hogs in Ohio poses a significant threat to agriculture, natural ecosystems, and human safety. Their rapid spread highlights the importance of a multi-pronged approach to management, including public awareness, trapping and removal, hunting, public-private partnerships, and ongoing research. By understanding the challenges posed by feral hogs and implementing effective control measures, Ohio can mitigate their impact and protect its valuable resources for future generations.


.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Spread of Feral Hogs in Ohio: A Growing Threat to Agriculture and Ecology. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!