The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power
Related Articles: The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power
- 3.1 Tracing the Borders of Wessex: A Chronological Journey
- 3.2 The Importance of the Wessex Map: A Window into History
- 3.3 Examining the Map: Key Features and Significance
- 3.4 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Wessex
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding the Map of Wessex
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Legacy of Power and Influence
- 4 Closure
The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power
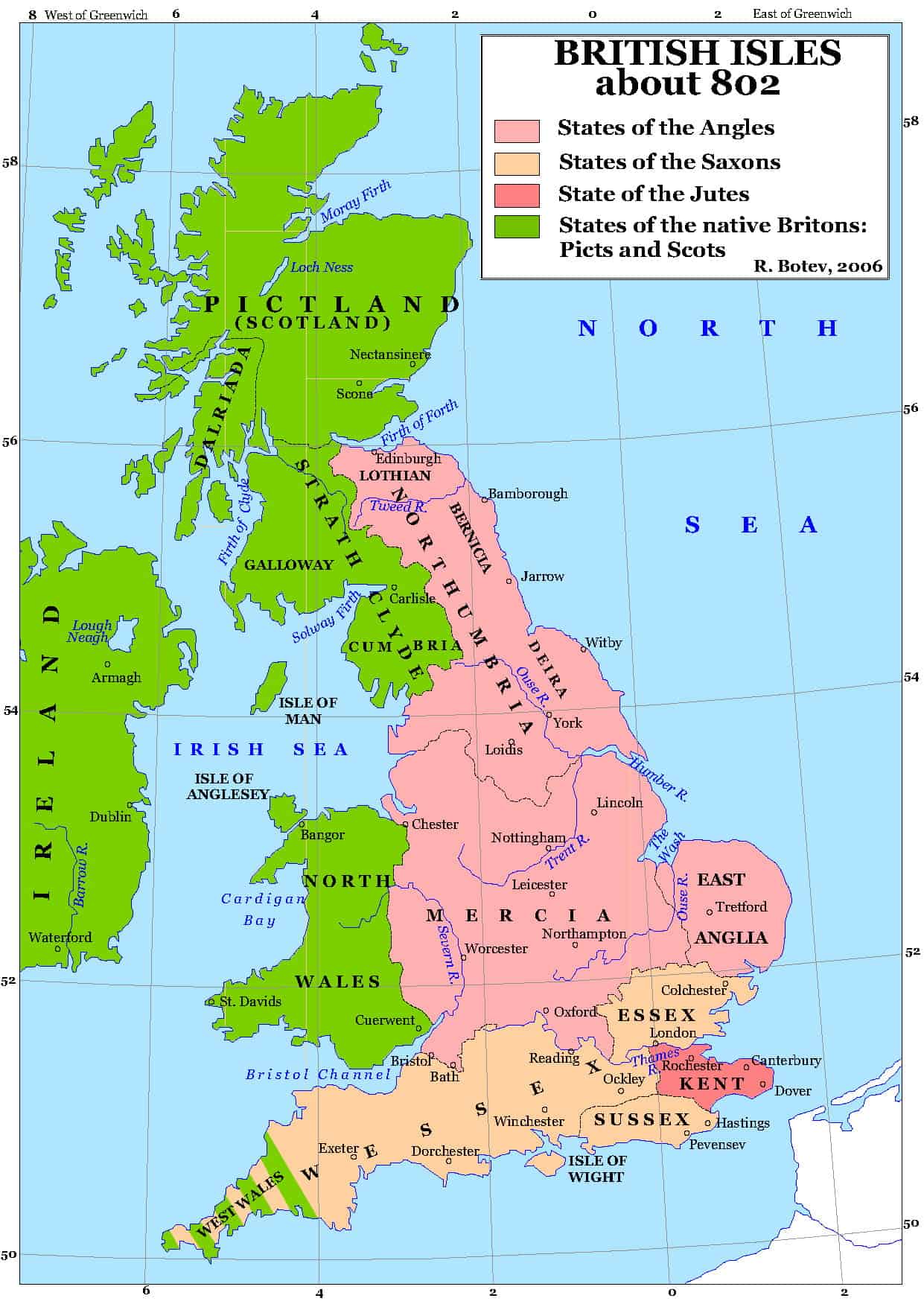
The Kingdom of Wessex, a pivotal entity in the tapestry of Anglo-Saxon England, played a crucial role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of the British Isles. Its geographical boundaries, constantly evolving through centuries of conflict and expansion, offer a fascinating window into the dynamics of early medieval England. This article delves into the map of Wessex, analyzing its evolution, key features, and significance in understanding the rise of English power.
Tracing the Borders of Wessex: A Chronological Journey
The map of Wessex, unlike a fixed geographical entity, underwent significant transformations over its existence. The early stages of the kingdom, around the 5th century, saw Wessex emerge as a small, independent realm in the south of England. Its initial core territory encompassed the modern counties of Hampshire, Wiltshire, and Dorset, encompassing the fertile lands of the Hampshire Downs and the chalk hills of Salisbury Plain.
The 7th century witnessed the kingdom’s expansion, driven by the ambition of its rulers. Wessex gradually incorporated the counties of Berkshire, Somerset, and parts of Devon, extending its influence westward and northward. This period saw the rise of powerful kings like Cenwalh and Ine, who secured victories against rival Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and consolidated Wessex’s position as a dominant force in the south.
The 8th and 9th centuries marked a period of turbulent conflict, with Wessex facing the constant threat of Viking invasions. Under the leadership of King Egbert, Wessex emerged victorious from these conflicts, establishing itself as the leading Anglo-Saxon kingdom. Egbert’s successors, notably Alfred the Great, further expanded Wessex’s boundaries, pushing the Viking threat back and forging a unified Anglo-Saxon England.
By the 10th century, Wessex had reached its zenith, encompassing a vast territory stretching from the English Channel to the River Thames. This period saw the reign of Æthelstan, who is credited with unifying England under Wessex’s rule, a watershed moment in English history. The map of Wessex during this era reflected the kingdom’s dominance, encompassing most of modern-day England, with the exception of the north, which remained under the control of the Vikings.
The Importance of the Wessex Map: A Window into History
The map of Wessex holds immense historical significance, providing valuable insights into the socio-political landscape of Anglo-Saxon England.
-
Territorial Expansion and Power Dynamics: The evolution of the map of Wessex reflects the kingdom’s dynamic growth and its ability to overcome challenges. It reveals the strategic importance of key geographic features, such as the River Thames, the English Channel, and the chalk hills, which provided natural defenses and resources.
-
Cultural and Linguistic Influence: The expansion of Wessex, particularly under Alfred the Great, led to the spread of West Saxon culture and language across England. This cultural influence, evident in literature, laws, and even place names, is reflected in the map’s boundaries, highlighting the extent of Wessex’s dominance.
-
Military Strategy and Defense: The map of Wessex reveals the kingdom’s strategic positioning, highlighting its vulnerability to Viking raids from the east coast and its strength in defending its southern borders. It also provides valuable insight into the military tactics employed by Wessex’s rulers, such as the use of fortified burhs and the development of a strong navy.
-
Administrative Structures: The map of Wessex illustrates the kingdom’s administrative organization, highlighting the importance of key towns, such as Winchester, which served as the capital, and the development of shire systems for governance. These structures laid the foundation for the administrative framework of later English kingdoms.
-
Religious and Cultural Centers: The map of Wessex reveals the location of important religious centers, such as the Abbey of Glastonbury and the Cathedral of Winchester, which played a significant role in the spread of Christianity and the development of Anglo-Saxon culture.
Examining the Map: Key Features and Significance
The map of Wessex reveals several key features that are crucial to understanding the kingdom’s history and significance:
-
The River Thames: The River Thames, a natural barrier and a vital trade route, formed a significant boundary between Wessex and the kingdoms to the north. It played a crucial role in Wessex’s expansion, providing access to trade routes and strategic control over key territories.
-
The English Channel: The English Channel, a natural defense against invasions from the continent, provided Wessex with a strategic advantage in protecting its southern borders. The kingdom’s naval strength, developed during the Viking raids, allowed it to control the Channel and secure its maritime trade.
-
The Chalk Hills: The chalk hills of southern England, including the Hampshire Downs and the Salisbury Plain, provided fertile land for agriculture and natural defenses against invaders. These regions were strategically important for Wessex, providing resources and a strong base for military operations.
-
The Burhs: The fortified burhs, strategically located across Wessex, played a vital role in defending the kingdom against Viking raids. These fortified settlements provided refuge for local communities and served as military bases for Wessex’s forces.
-
The Royal Palace at Winchester: Winchester, the capital of Wessex, housed the royal palace and served as the kingdom’s administrative center. Its location in the heart of Wessex, within easy reach of key trade routes and military bases, reflects its importance as a hub of political and economic activity.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Wessex
1. What were the main challenges faced by the Kingdom of Wessex?
The Kingdom of Wessex faced several challenges throughout its history, including:
-
Viking Raids: Wessex endured frequent attacks from Viking invaders, particularly during the 9th century. These raids threatened the kingdom’s stability and forced Wessex to develop a strong military and defensive strategy.
-
Internal Conflicts: Wessex also faced internal conflicts with other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, such as Mercia and Northumbria. These conflicts often arose from territorial disputes and struggles for power, shaping the political landscape of Anglo-Saxon England.
-
Succession Disputes: Disputes over the succession to the throne were a recurring problem within Wessex, leading to internal power struggles and instability.
2. How did Alfred the Great contribute to the development of Wessex?
Alfred the Great, who reigned from 871 to 899, is considered a pivotal figure in Wessex’s history. He played a crucial role in:
-
Defeating the Vikings: Alfred successfully repelled Viking invasions, securing Wessex’s independence and laying the foundation for a unified England.
-
Promoting Education and Culture: Alfred fostered the development of education and culture, encouraging the translation of important texts into Old English and promoting literacy within the kingdom.
-
Building a Strong Navy: Alfred recognized the importance of a strong navy in protecting Wessex’s coastline and securing its trade routes. He established a fleet of ships that played a crucial role in defending the kingdom against Viking attacks.
3. What was the significance of the Battle of Edington in 878?
The Battle of Edington, a decisive victory for Alfred the Great over the Viking leader Guthrum, marked a turning point in the history of Wessex. It resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Wedmore, which established a boundary between Wessex and the Viking-controlled Danelaw, effectively halting the Viking advance and securing Wessex’s independence.
4. How did the Kingdom of Wessex influence the development of England?
The Kingdom of Wessex played a crucial role in shaping the political, cultural, and linguistic landscape of England. Its expansion and the unification of England under Wessex’s rule laid the foundation for a unified English identity and the development of English institutions. Wessex’s cultural influence, particularly in literature, law, and language, left an enduring legacy on English society.
5. What are some of the key sources of information about the Kingdom of Wessex?
Several sources provide valuable insights into the history of the Kingdom of Wessex, including:
-
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle: This historical record, compiled by Anglo-Saxon monks, provides a detailed account of Wessex’s history, covering events from the 5th to the 11th centuries.
-
Archaeological Evidence: Archaeological excavations have unearthed numerous artifacts and settlements from the Wessex period, providing valuable information about the kingdom’s culture, economy, and daily life.
-
Literary Sources: Literary works from the Anglo-Saxon period, such as Beowulf and the epic poem "The Battle of Maldon," offer insights into the values, beliefs, and social structures of Wessex.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Wessex
-
Use a Historical Atlas: A historical atlas provides a comprehensive overview of the changing boundaries of Wessex, allowing you to trace its evolution over time.
-
Study Key Battles and Events: Understanding the key battles and events that shaped Wessex’s history, such as the Battle of Edington and the Viking raids, will provide context for the map’s changes and the kingdom’s strategic decisions.
-
Identify Key Geographic Features: Recognizing the importance of the River Thames, the English Channel, and the chalk hills in shaping Wessex’s history and influencing its strategic decisions will provide a deeper understanding of the map’s significance.
-
Research Important Figures: Learning about the lives and accomplishments of key figures in Wessex’s history, such as Alfred the Great, Egbert, and Æthelstan, will provide valuable insight into the kingdom’s political and cultural development.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Power and Influence
The map of Wessex, a testament to the kingdom’s rise and fall, provides a fascinating glimpse into the complex tapestry of Anglo-Saxon England. It highlights the kingdom’s remarkable expansion, its resilience in the face of Viking invasions, and its lasting influence on the development of English culture, language, and institutions. The legacy of Wessex, evident in the political and cultural landscape of modern England, continues to inspire and fascinate historians and enthusiasts alike.






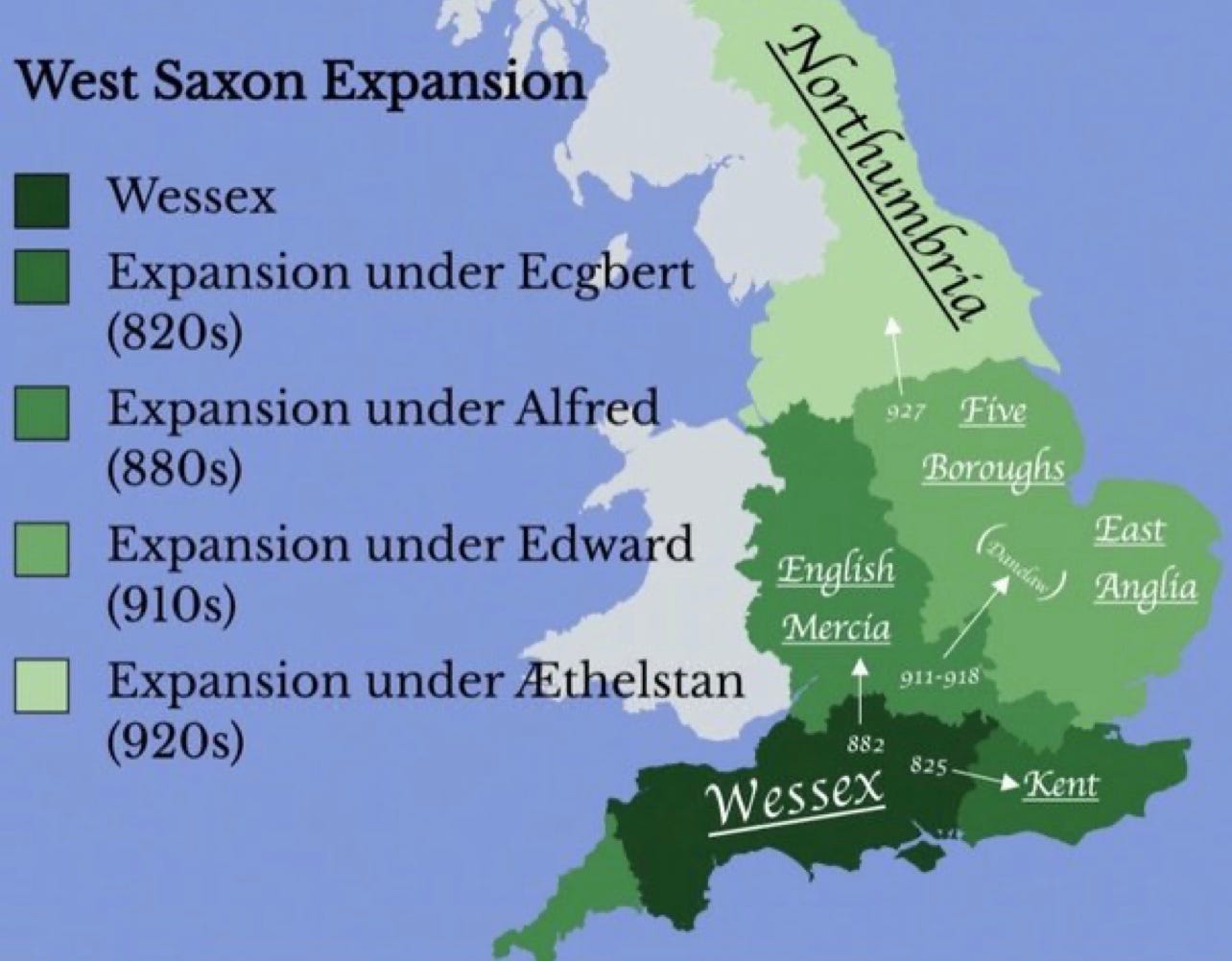
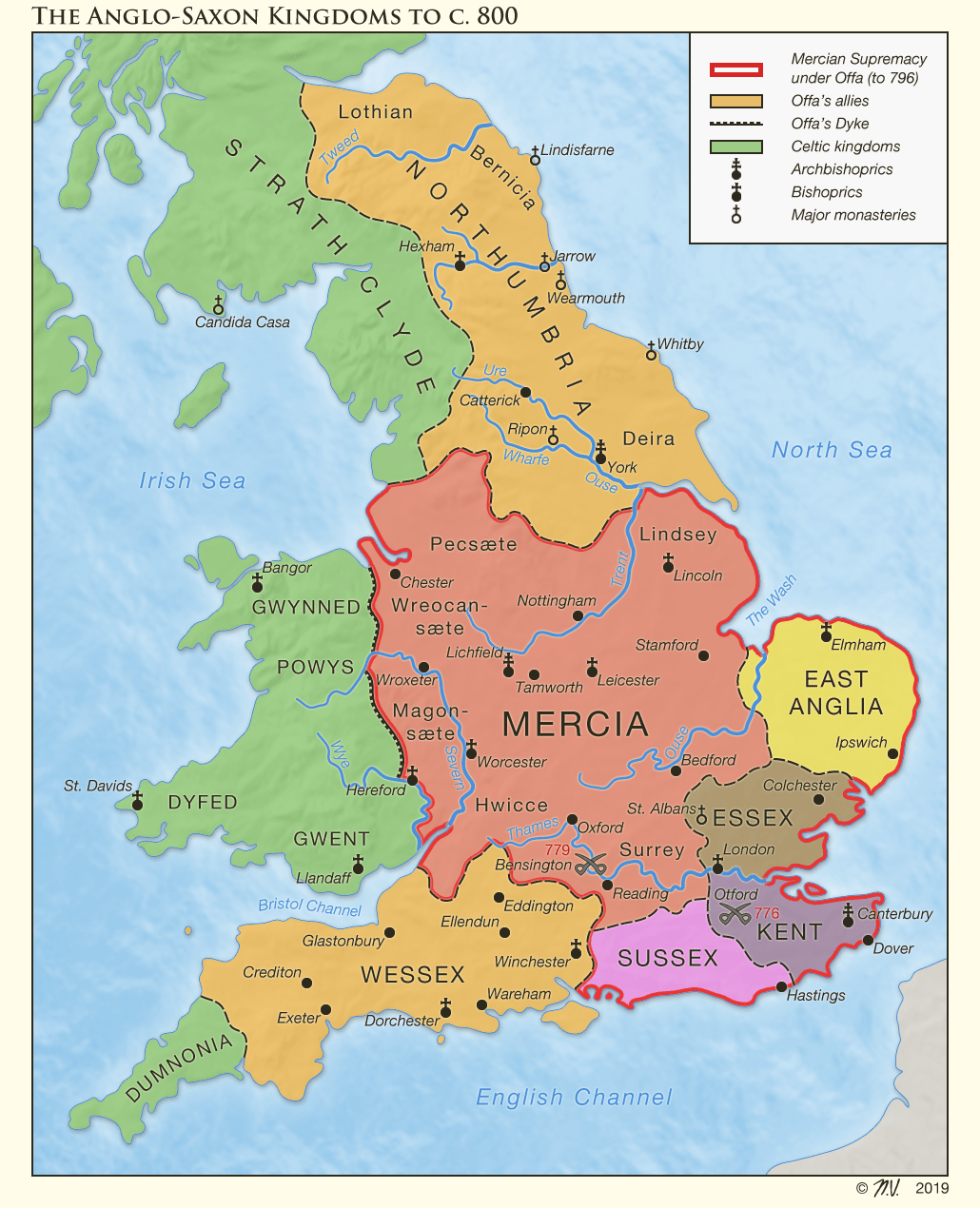
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Kingdom of Wessex: A Map of Anglo-Saxon Power. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!