The Anaconda Plan: A Strategic Blueprint for Union Victory in the American Civil War
Related Articles: The Anaconda Plan: A Strategic Blueprint for Union Victory in the American Civil War
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Anaconda Plan: A Strategic Blueprint for Union Victory in the American Civil War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Anaconda Plan: A Strategic Blueprint for Union Victory in the American Civil War
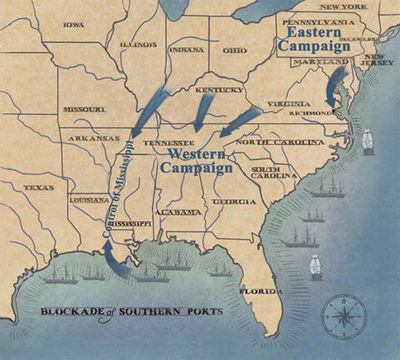
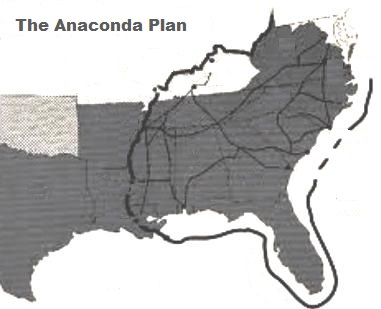
The American Civil War, a tumultuous period in United States history, witnessed the clash of ideologies and the struggle for national unity. Amidst the chaos and bloodshed, the Union government devised a comprehensive strategy to subdue the Confederate States of America: the Anaconda Plan. This strategic blueprint, named after the constricting South American snake, aimed to cripple the Confederacy by choking off its resources and isolating its territory.
Understanding the Anaconda Plan’s Core Principles:
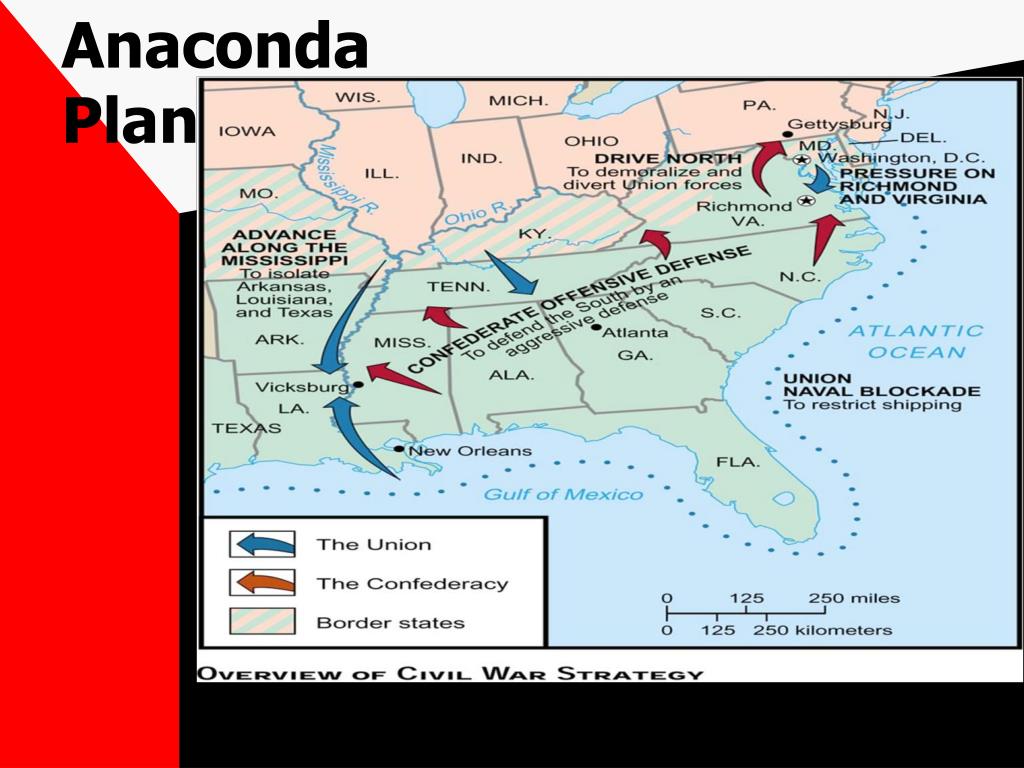
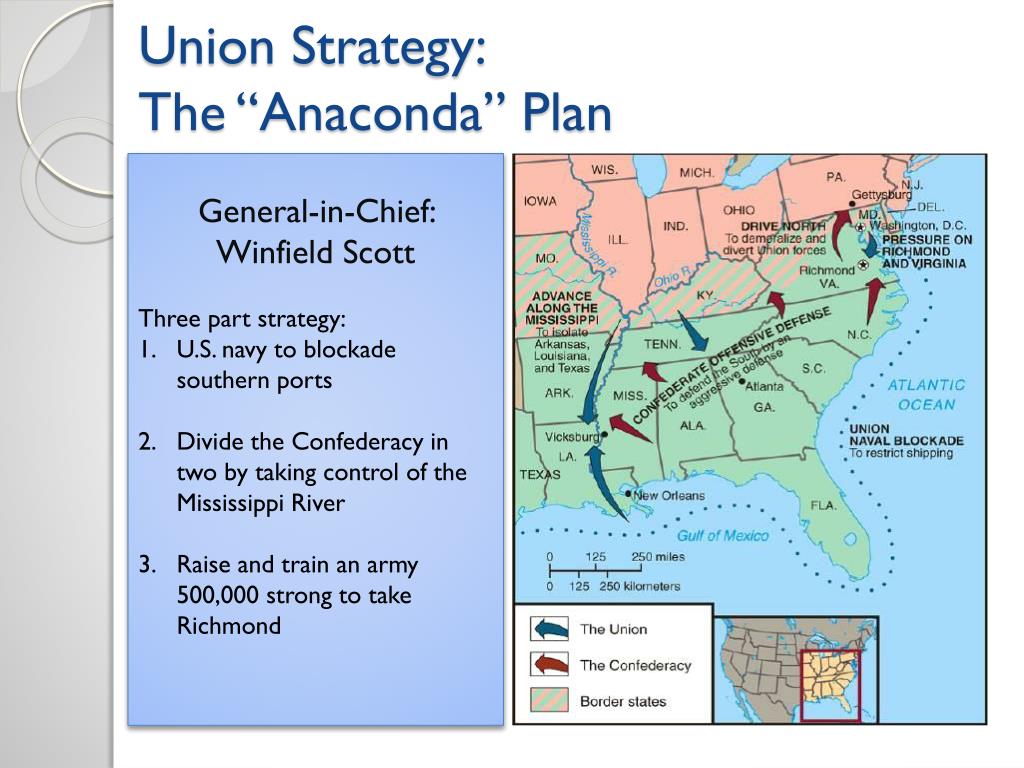
The Anaconda Plan, conceived by Winfield Scott, the Union’s Commanding General, was a multi-pronged strategy that relied on naval blockade, land-based offensives, and economic pressure. Its central tenets were:
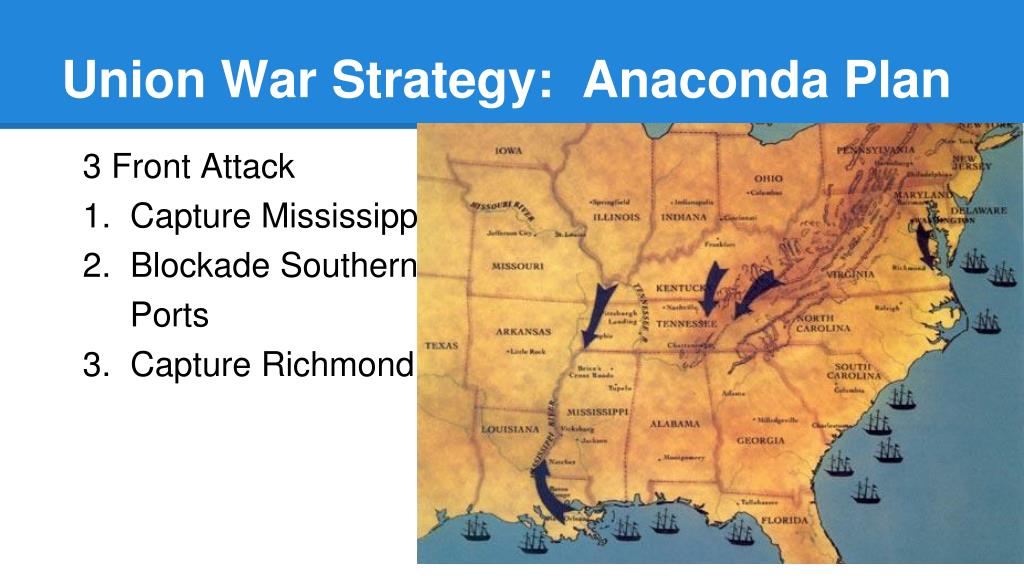
- Naval Blockade: The Union Navy would establish a tight blockade along the Confederate coastline, preventing the flow of supplies, goods, and resources into the Confederacy. This would cripple the South’s economy and hinder its ability to sustain its war effort.
- Control of the Mississippi River: The Mississippi River served as a vital artery for the Confederacy, connecting its western territories to the east. The Union aimed to seize control of the river, severing this crucial link and isolating the Confederacy’s western states.
- Land-Based Offensives: Simultaneous offensives would be launched from various directions, aiming to capture key Confederate cities and strategic locations. This would gradually erode Confederate territory and weaken its defenses.
- Economic Pressure: The Union aimed to undermine the Confederate economy through a combination of blockade, disruption of trade, and the capture of key economic centers. This would weaken the Confederacy’s ability to fund its war effort.
The Implementation of the Anaconda Plan:
The Anaconda Plan was implemented in stages, with the initial focus on establishing the naval blockade. The Union Navy, under the leadership of Flag Officer Samuel F. Du Pont, began the blockade in 1861, gradually tightening its grip on Confederate ports. This proved to be a major success, significantly reducing the flow of goods and resources to the South.
Simultaneously, Union forces launched land-based offensives. The capture of Fort Henry and Fort Donelson in 1862 opened up the Tennessee River, allowing Union forces to advance deeper into the South. The Union’s victory at Shiloh in the same year solidified its control over western Tennessee.
The control of the Mississippi River was a crucial objective. The Union’s capture of New Orleans in 1862 was a major blow to the Confederacy, securing a vital port and opening up the river to Union shipping. The capture of Vicksburg in 1863 finally secured the Mississippi River, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two.
Challenges and Criticisms:
The Anaconda Plan faced numerous challenges. The vastness of the Confederate territory, the determination of Confederate forces, and the limitations of Union resources posed significant hurdles. Critics argued that the plan was slow, passive, and relied too heavily on a naval blockade, which was vulnerable to Confederate attacks.
The Anaconda Plan’s Impact:
Despite the challenges, the Anaconda Plan proved to be a highly effective strategy. The naval blockade choked off the Confederate economy, while land-based offensives gradually eroded Confederate territory. The control of the Mississippi River severed a vital link between the Confederacy’s western and eastern states, further isolating and weakening the South.
The Anaconda Plan, though slow and criticized by some, played a crucial role in the Union’s eventual victory. It demonstrated the importance of strategic planning, resource management, and a comprehensive approach to warfare.
FAQs About the Anaconda Plan:
Q: What was the primary objective of the Anaconda Plan?
A: The primary objective of the Anaconda Plan was to cripple the Confederacy by choking off its resources, isolating its territory, and ultimately forcing its surrender.
Q: What were the main components of the Anaconda Plan?
A: The main components included a naval blockade, control of the Mississippi River, land-based offensives, and economic pressure.
Q: Was the Anaconda Plan successful?
A: The Anaconda Plan, while initially criticized for its slow pace, proved to be a highly effective strategy. It contributed significantly to the Union’s eventual victory.
Q: What were the major challenges faced by the Anaconda Plan?
A: The challenges included the vastness of Confederate territory, the determination of Confederate forces, and the limitations of Union resources.
Q: What are some of the criticisms of the Anaconda Plan?
A: Some critics argued that the plan was slow, passive, and relied too heavily on a naval blockade, which was vulnerable to Confederate attacks.
Tips for Studying the Anaconda Plan:
- Visualize the Strategy: Use maps and diagrams to understand the geographical scope and key locations involved in the Anaconda Plan.
- Focus on the Key Components: Analyze the specific roles of the naval blockade, the Mississippi River, land-based offensives, and economic pressure.
- Study the Major Battles and Campaigns: Research the key battles and campaigns that were part of the Anaconda Plan, such as the capture of New Orleans, Vicksburg, and Fort Henry.
- Consider the Impact on the Civilian Population: Explore how the Anaconda Plan affected the lives of civilians in both the North and the South.
- Compare and Contrast with Other Strategies: Analyze the Anaconda Plan in relation to other Union strategies, such as the March to the Sea by General Sherman.
Conclusion:
The Anaconda Plan stands as a testament to the power of strategic planning and the importance of comprehensive warfare. Its success, though achieved gradually and amidst significant challenges, ultimately contributed to the Union’s victory in the American Civil War. The Anaconda Plan’s legacy continues to be studied and analyzed by historians and military strategists, offering valuable insights into the complexities of warfare and the importance of strategic thinking.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Anaconda Plan: A Strategic Blueprint for Union Victory in the American Civil War. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!