Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the English Railway Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the English Railway Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the English Railway Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the English Railway Map
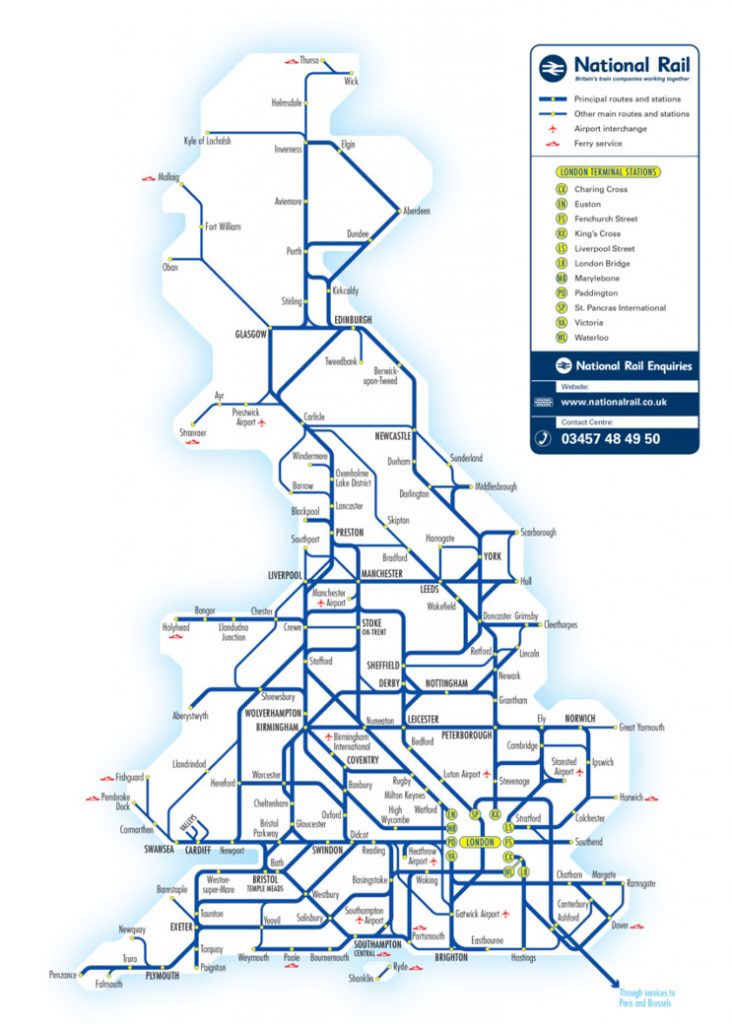
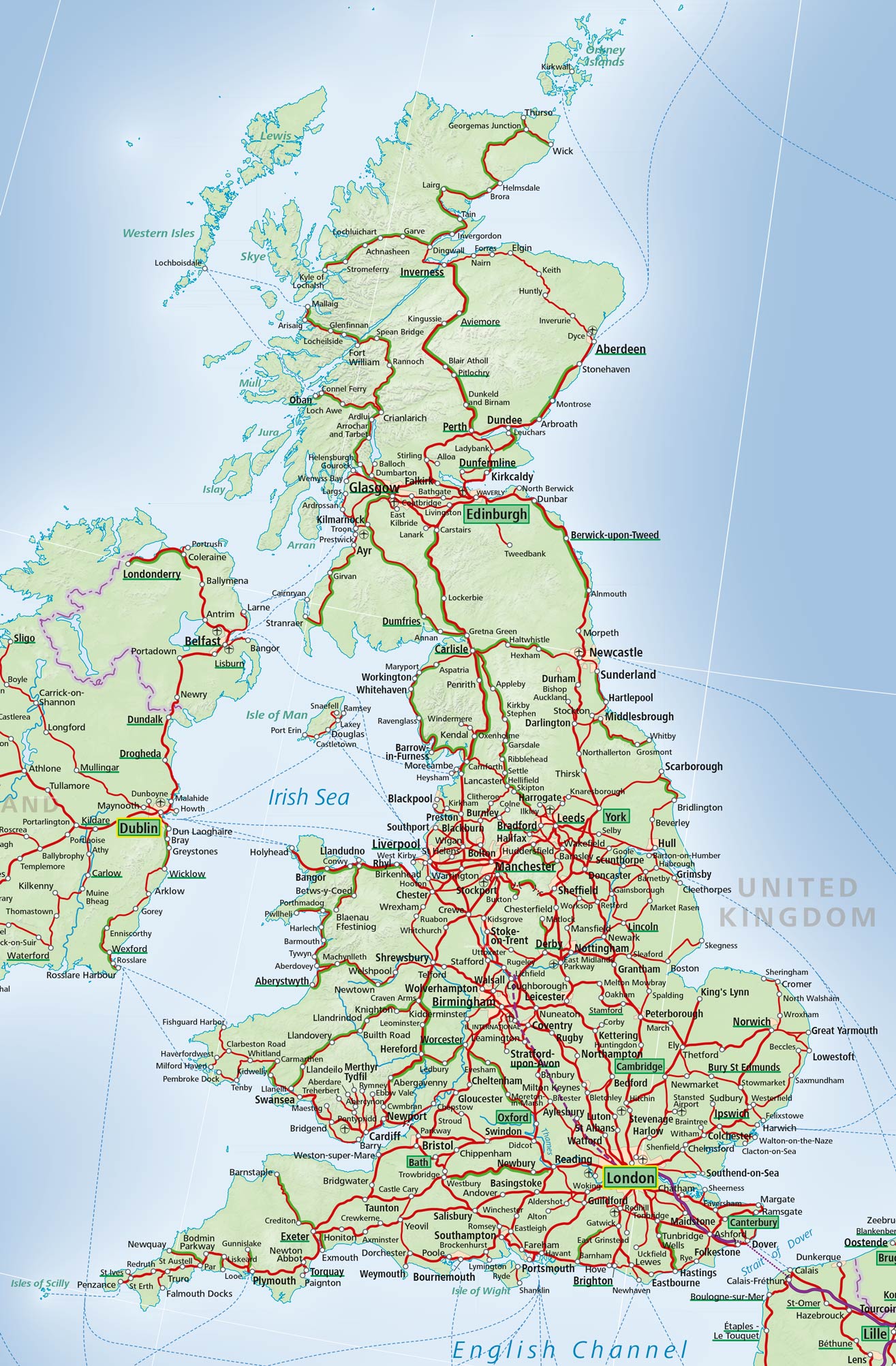
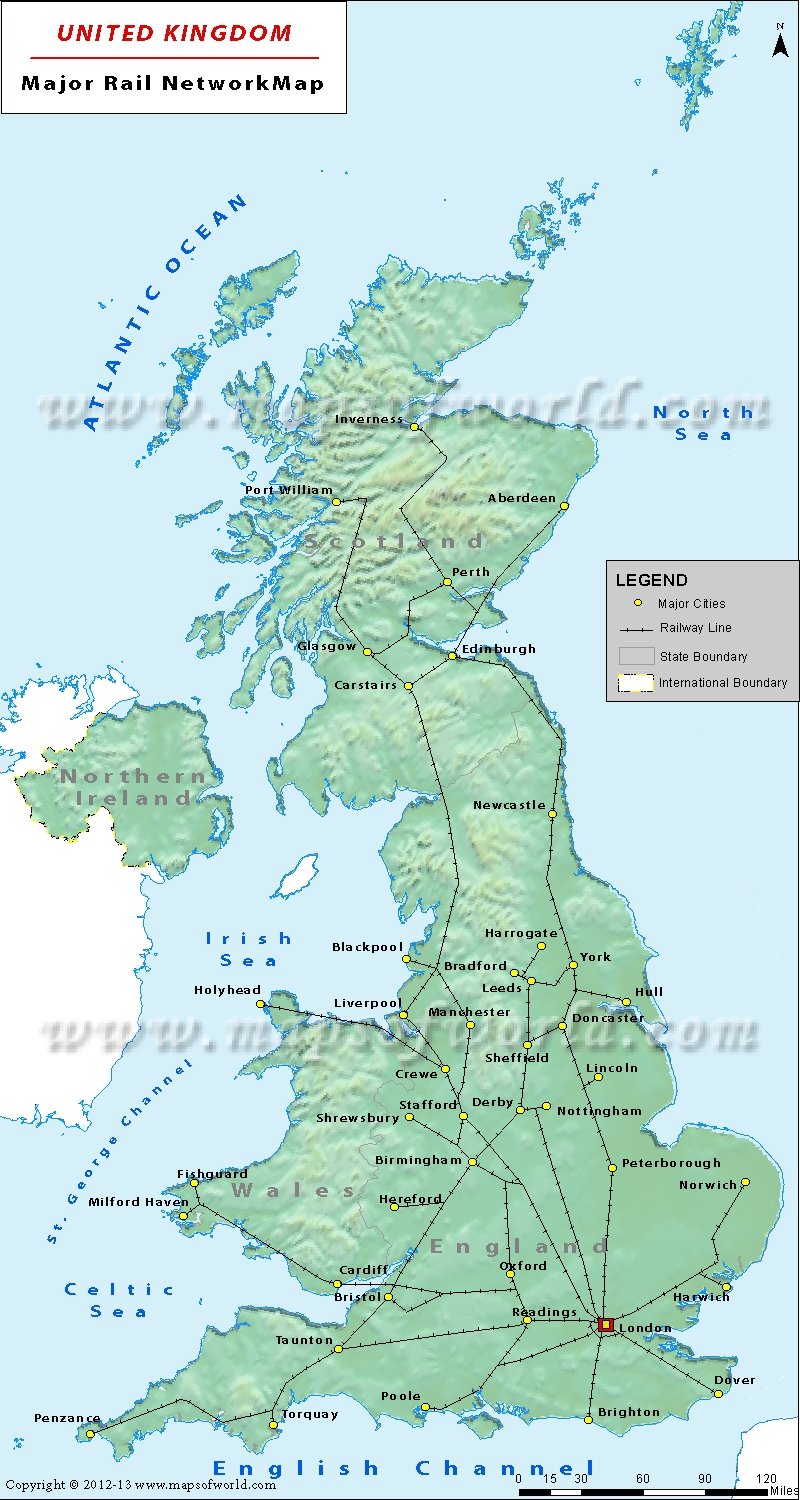
The English railway network, a sprawling web of steel and concrete, is a vital artery for the nation’s economy and social fabric. Understanding its intricate map is crucial for anyone planning a journey within the United Kingdom, whether for business, leisure, or daily commute. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of the English railway map, exploring its history, key features, and practical applications.
A Historical Perspective:
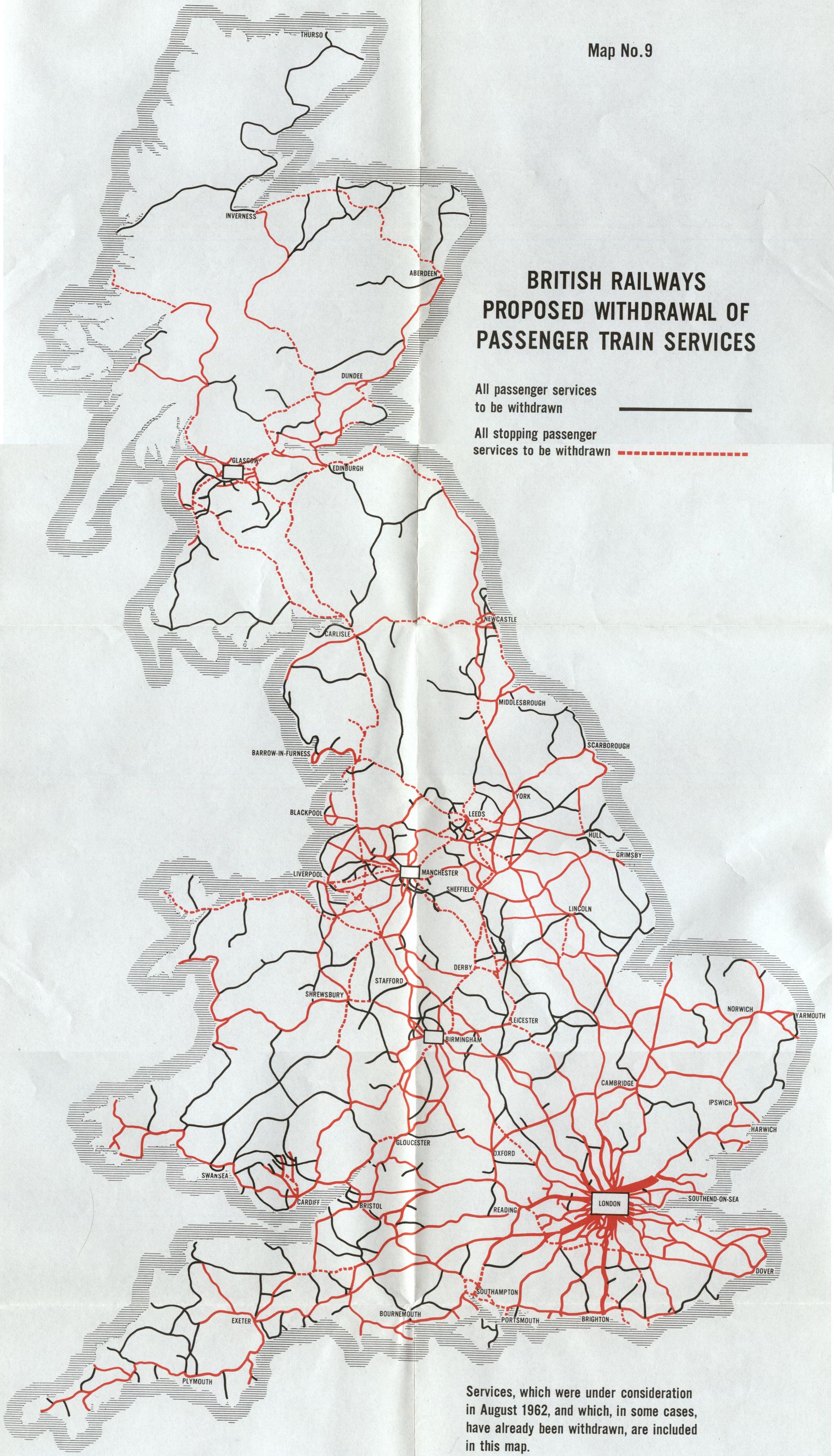
The origins of the English railway map can be traced back to the early 19th century, a period marked by rapid industrialization and technological advancements. The first railway line, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, opened in 1830, ushering in an era of unprecedented connectivity. This marked the beginning of a network that would eventually crisscross the country, connecting major cities, towns, and villages.
The early railway map was a relatively simple affair, with lines radiating outward from major hubs. However, as the network expanded, the map became increasingly complex, reflecting the growth of industrial centers and the need for efficient transportation. The Victorian era witnessed the construction of numerous lines, many of which remain operational today, forming the backbone of the modern railway network.
Key Features and Terminology:
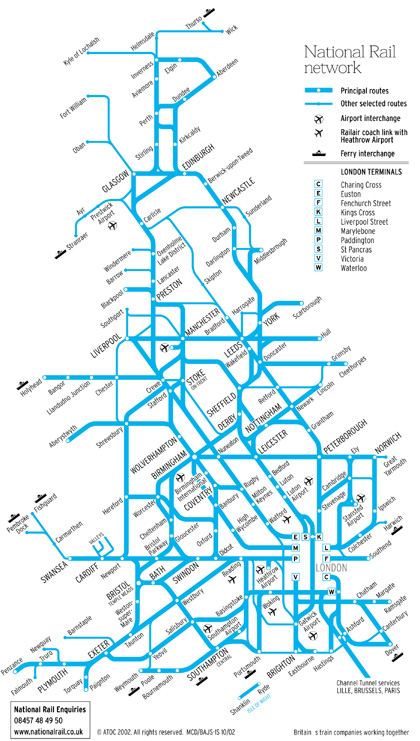
The English railway map is a complex tapestry of lines, stations, and interchanges. Understanding the key features and terminology is essential for effective navigation.
1. Lines:
- Main Lines: These are the primary routes connecting major cities and towns, typically characterized by high-speed services and frequent departures.
- Branch Lines: These lines extend from main lines to smaller towns and villages, offering connectivity to areas that might otherwise be isolated.
- Cross-Country Lines: These lines connect major cities across the country, providing alternative routes and reducing travel time.
- Commuter Lines: These lines focus on transporting passengers to and from major urban centers, often with frequent and fast services during peak hours.
2. Stations:
- Major Stations: These are large stations serving major cities and towns, often with multiple platforms, extensive facilities, and connections to other transport modes.
- Regional Stations: These stations serve smaller towns and villages, often with limited facilities and fewer services.
- Interchange Stations: These stations allow passengers to transfer between different lines, providing connections to other destinations.
3. Interchanges:
- Hub Stations: These are major stations with numerous connections to other lines, facilitating easy transfers between destinations.
- Junction Stations: These stations mark the point where lines diverge, offering multiple routes to different destinations.
- Cross-Platform Interchanges: These interchanges allow passengers to change lines without leaving the station, ensuring a seamless transition.
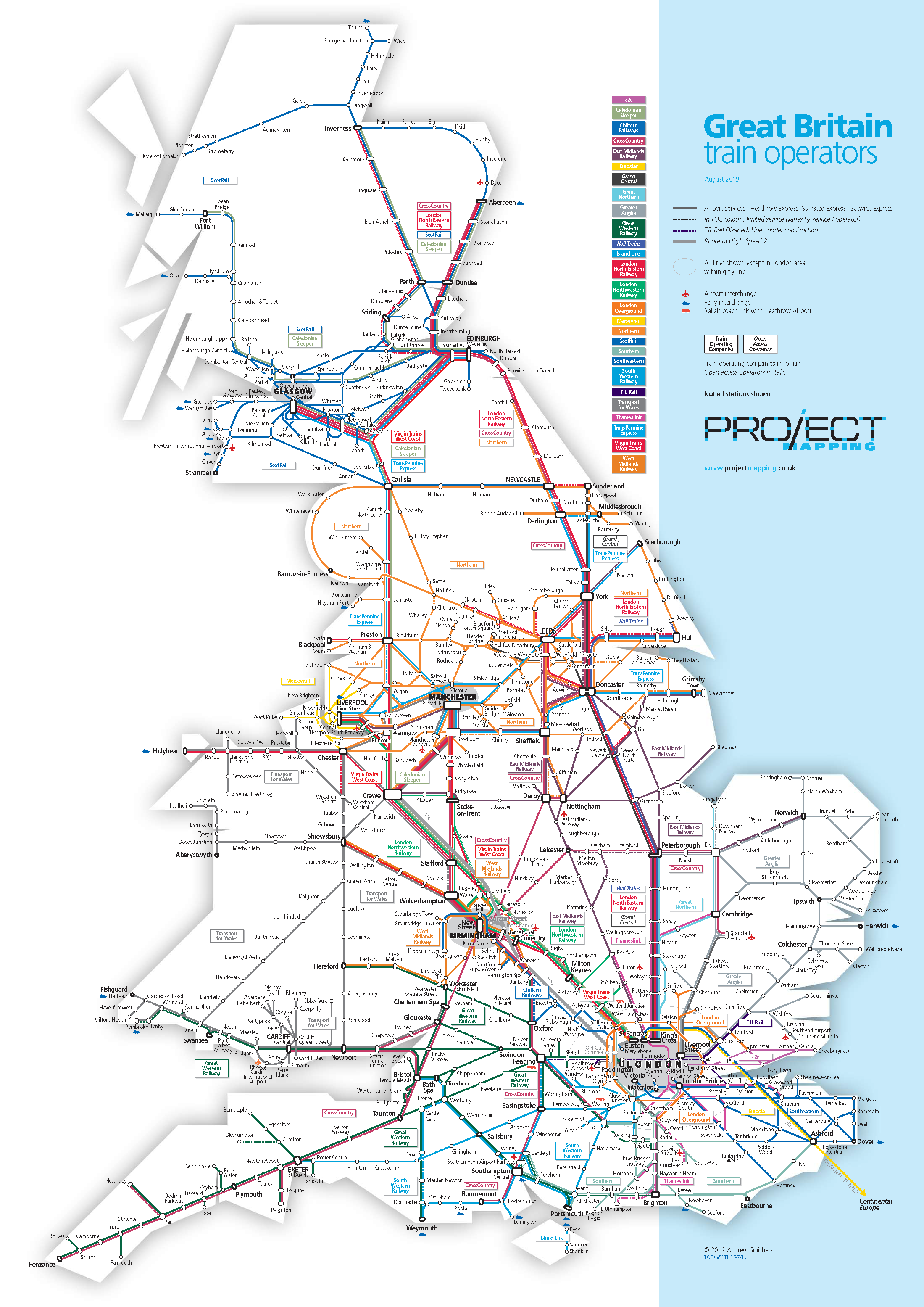
4. Operators:
The English railway network is operated by a multitude of companies, each with its own geographic area of responsibility and service offerings. Understanding the different operators is crucial for planning journeys and purchasing tickets.
5. Timetables:
Timetables are essential for planning journeys and ensuring punctual travel. They provide information on train schedules, departure and arrival times, and service frequencies.
6. Fares:
Ticket prices vary depending on the distance travelled, time of day, and type of ticket purchased. Advanced booking and off-peak travel often result in lower fares.
7. Ticketing Options:
The English railway network offers a variety of ticketing options, including:
- Single Tickets: Valid for a single journey between two specified stations.
- Return Tickets: Valid for a round trip between two specified stations.
- Day Tickets: Valid for unlimited travel on a specific day within a specified region.
- Season Tickets: Valid for unlimited travel on a specific route for a specified period.
Navigating the Map: Practical Applications:
The English railway map is an indispensable tool for planning journeys and exploring the country. Here are some practical applications:
1. Journey Planning:
- Identify your starting and destination stations: Locate your starting point and final destination on the map.
- Determine the optimal route: Choose the most convenient and efficient route based on factors such as travel time, cost, and service frequency.
- Check for interchanges: If your journey involves multiple lines, identify the necessary interchanges and ensure seamless transitions.
- Consult timetables: Verify train schedules, departure and arrival times, and service frequencies to ensure punctual travel.
2. Exploring Destinations:
- Discover hidden gems: The railway map can reveal lesser-known destinations and attractions, offering opportunities to explore beyond the well-trodden tourist paths.
- Plan day trips: Utilize the map to plan day trips to nearby towns and villages, experiencing the diverse landscapes and culture of England.
- Explore historical sites: The railway network connects numerous historical sites, offering opportunities to delve into the rich history of England.
3. Understanding Regional Variations:
The English railway network is characterized by regional variations in service frequency, infrastructure, and ticketing options. Understanding these variations is crucial for efficient travel planning.
- London Underground: The London Underground, also known as the Tube, is a separate network with its own map and ticketing system.
- Rural Lines: Rural lines often have less frequent services and fewer amenities compared to main lines.
- Regional Operators: Different operators may offer different levels of service and amenities, so it is important to compare options before booking.
FAQs about the English Railway Map:
1. What is the best way to navigate the English railway map?
- Online resources: Websites like National Rail Enquiries and Trainline offer interactive maps, journey planners, and real-time information.
- Mobile apps: Numerous mobile apps, such as the National Rail Enquiries app and Trainline app, provide comprehensive mapping features, journey planning tools, and live updates.
- Printed maps: Printed maps are available at railway stations and tourist information centers, offering a visual overview of the network.
2. How can I find the most affordable fares?
- Advance booking: Booking tickets in advance, especially for off-peak travel, often results in lower fares.
- Off-peak travel: Traveling during off-peak hours, typically outside of rush hour, can lead to significant savings.
- Group tickets: Consider purchasing group tickets if traveling with a group of people, as they often offer discounted fares.
- Railcards: Various railcards are available, offering discounts on fares for specific groups, such as students, seniors, and families.
3. What are the key considerations for planning a journey on the English railway network?
- Travel time: Factor in travel time, including potential delays, to ensure ample time to reach your destination.
- Interchanges: Identify any necessary interchanges and allow sufficient time for transfers.
- Service frequency: Check the frequency of services, especially during off-peak hours or on weekends.
- Accessibility: Consider accessibility requirements for passengers with disabilities or mobility issues.
- Luggage: Ensure your luggage meets the size and weight restrictions for the chosen train service.
Tips for Utilizing the English Railway Map:
- Plan ahead: Plan your journey in advance, considering travel time, interchanges, and service frequency.
- Check for disruptions: Be aware of potential disruptions, such as engineering works or strikes, and plan accordingly.
- Purchase tickets in advance: Booking tickets in advance can save you money and guarantee your seat.
- Arrive early: Arrive at the station early to allow for potential delays and ensure you catch your train.
- Keep your ticket handy: Ensure you have your ticket readily available for inspection by staff.
Conclusion:
The English railway map is a complex but essential tool for navigating the country’s intricate network. Understanding its key features, terminology, and practical applications can enhance travel experiences, ensuring efficient journeys and opportunities to explore the diverse landscapes and culture of England. By utilizing online resources, mobile apps, and printed maps, travelers can unlock the potential of the English railway network, making it a reliable and enjoyable means of transportation.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the English Railway Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
