Navigating the Political Landscape of Thailand: A Comprehensive Guide to its Administrative Divisions
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Thailand: A Comprehensive Guide to its Administrative Divisions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape of Thailand: A Comprehensive Guide to its Administrative Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape of Thailand: A Comprehensive Guide to its Administrative Divisions
Thailand, a vibrant Southeast Asian nation known for its rich culture, stunning landscapes, and bustling cities, boasts a complex political structure that reflects its unique history and evolution. Understanding the intricate web of its administrative divisions is crucial for navigating the country’s political, economic, and social dynamics. This comprehensive guide delves into the political map of Thailand, exploring its various levels of governance and their implications for the nation’s development.
A Glimpse into Thailand’s Administrative Hierarchy:
Thailand’s political map is characterized by a multi-tiered system of governance, with each level playing a distinct role in shaping the nation’s destiny. The hierarchy, starting from the broadest to the most localized level, comprises:
-
The Kingdom: Thailand is a constitutional monarchy, with the King serving as the head of state. The King holds a symbolic and revered position, acting as a unifying figure and upholding the nation’s traditions.
-
The Central Government: The executive branch of the government resides in Bangkok, the capital city. The Prime Minister, elected by the House of Representatives, leads the government and oversees the implementation of national policies.
-
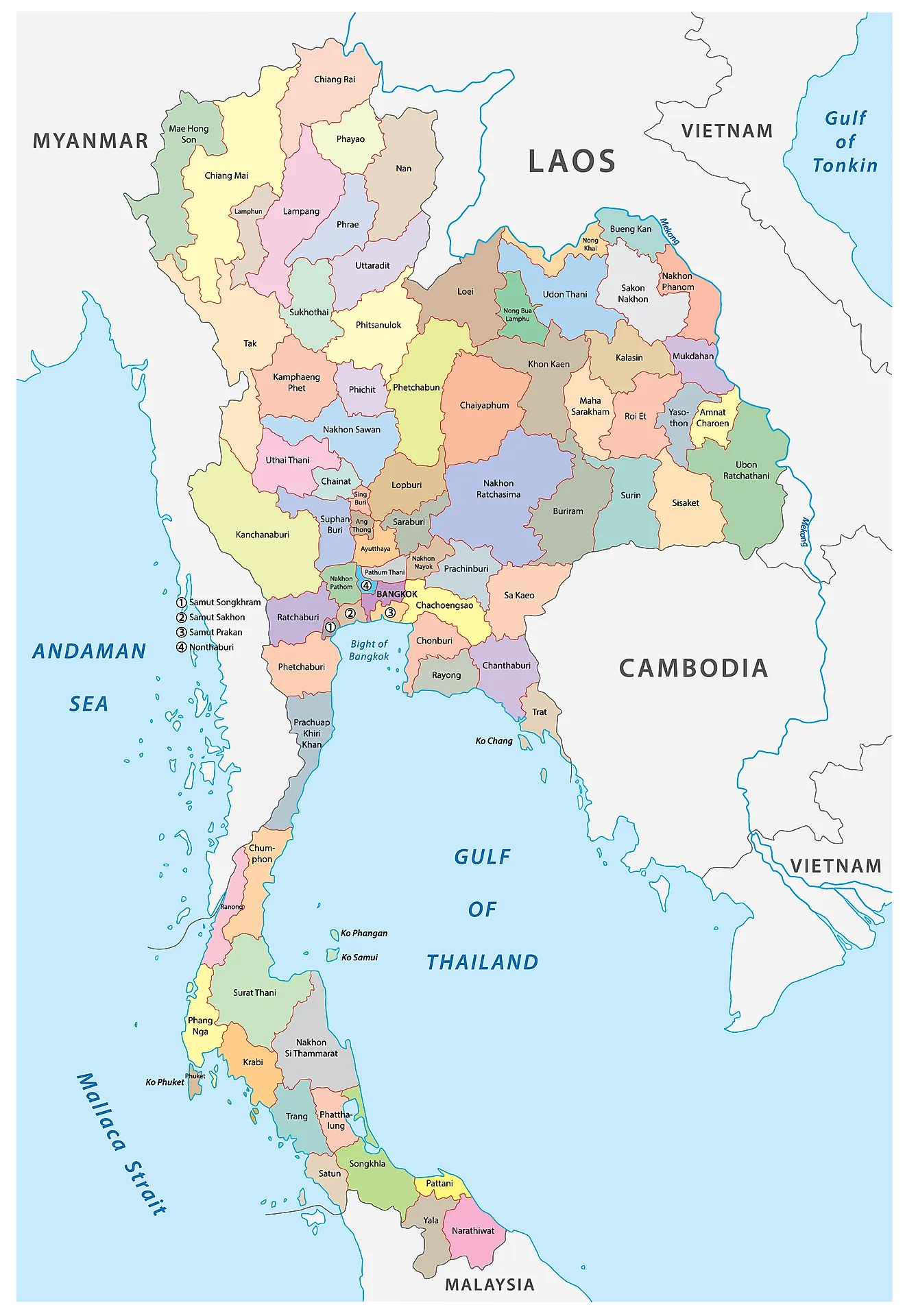
Provinces (Changwat): Thailand is divided into 76 provinces, each headed by a governor appointed by the Ministry of Interior. Provinces are further subdivided into districts (Amphoe).
-
Districts (Amphoe): Each province encompasses multiple districts, each led by a district officer (Nai Amphoe). Districts are responsible for administering local affairs within their boundaries.
-
Sub-districts (Tambon): Districts are further divided into sub-districts, each headed by a sub-district headman (Kamnan).
-
Villages (Muban): Sub-districts consist of several villages, each with a village headman (Phu Yai Ban) elected by the local community.
Understanding the Significance of Thailand’s Political Map:
The intricate network of administrative divisions plays a vital role in shaping Thailand’s political landscape. It serves several key functions:
-
Decentralization of Power: The multi-tiered system facilitates the decentralization of power, allowing for local communities to participate in decision-making processes that directly impact their lives.
-
Efficient Governance: The hierarchical structure enables the government to effectively manage and administer the nation’s resources, ensuring the smooth functioning of various services and programs.
-
Cultural Preservation: The division into provinces and districts allows for the preservation of diverse cultural traditions and local identities within the larger national framework.
-
Economic Development: The administrative divisions provide a framework for regional development initiatives, fostering economic growth and promoting equitable distribution of resources across the country.
-
Political Stability: The system of checks and balances, with power distributed among different levels of government, contributes to political stability and prevents the concentration of power in a single entity.
A Closer Look at Thailand’s Provinces:
Each of Thailand’s 76 provinces possesses a unique character, shaped by its geography, history, culture, and economic activities. Some notable provinces include:
-
Bangkok: The capital city and the nation’s economic and cultural hub, Bangkok is a bustling metropolis with a vibrant nightlife, world-class shopping, and renowned temples.
-
Chiang Mai: A popular tourist destination in northern Thailand, Chiang Mai is known for its ancient temples, lush mountains, and charming Old City.
-
Phuket: Located on the Andaman coast, Phuket is a renowned island paradise with pristine beaches, crystal-clear waters, and vibrant nightlife.
-
Ayutthaya: A historical city located north of Bangkok, Ayutthaya served as the capital of the Siamese Kingdom for over 400 years and is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
-
Krabi: A breathtaking province in southern Thailand, Krabi is renowned for its limestone cliffs, secluded beaches, and stunning islands.
FAQs about Thailand’s Political Map:
1. What are the main political parties in Thailand?
Thailand has a multi-party political system, with several prominent parties vying for power. Some of the major political parties include:
-
Pheu Thai Party: A center-left party that has been in power several times, advocating for social welfare and economic development.
-
Democrat Party: A center-right party that has traditionally been a strong opposition force, promoting free-market principles and conservative values.
-
Bhumjaithai Party: A center-right party with a focus on rural development and agriculture.
-
Palang Pracharath Party: A center-right party that supports the monarchy and promotes national security.
2. How does the Thai government function?
Thailand’s government operates under a constitutional monarchy system. The King is the head of state, while the Prime Minister, elected by the House of Representatives, leads the government. The legislature comprises the House of Representatives and the Senate. The judiciary is independent and responsible for interpreting the law.
3. What are the main challenges facing Thailand’s political system?
Thailand’s political system faces several challenges, including:
-
Political Instability: The country has experienced numerous coups and political upheavals, leading to periods of instability and uncertainty.
-
Corruption: Corruption remains a significant issue in Thailand, undermining public trust in government institutions.
-
Inequality: Despite economic progress, significant income inequality persists, leading to social tensions and unrest.
-
Military Influence: The military continues to exert considerable influence on Thai politics, sometimes intervening directly in government affairs.
Tips for Understanding Thailand’s Political Map:
-
Consult reliable sources: Utilize reputable news outlets, academic journals, and government websites for accurate information about Thailand’s political system.
-
Engage with local experts: Seek insights from Thai academics, political analysts, and community leaders to gain a deeper understanding of the nuances of Thai politics.
-
Travel to different regions: Visiting various provinces and interacting with local communities can provide valuable insights into the diverse political landscape of Thailand.
-
Follow Thai media: Staying informed about current events and political developments through Thai news sources offers a firsthand perspective on the country’s political dynamics.
Conclusion:
Thailand’s political map is a complex tapestry woven from its history, culture, and socio-economic realities. Understanding its intricate administrative divisions and the dynamics of power distribution is essential for comprehending the nation’s political landscape. While challenges remain, the Thai people continue to navigate their political journey, striving for stability, progress, and a brighter future for their beloved nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape of Thailand: A Comprehensive Guide to its Administrative Divisions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!