Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to the Orion Star Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to the Orion Star Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to the Orion Star Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to the Orion Star Map
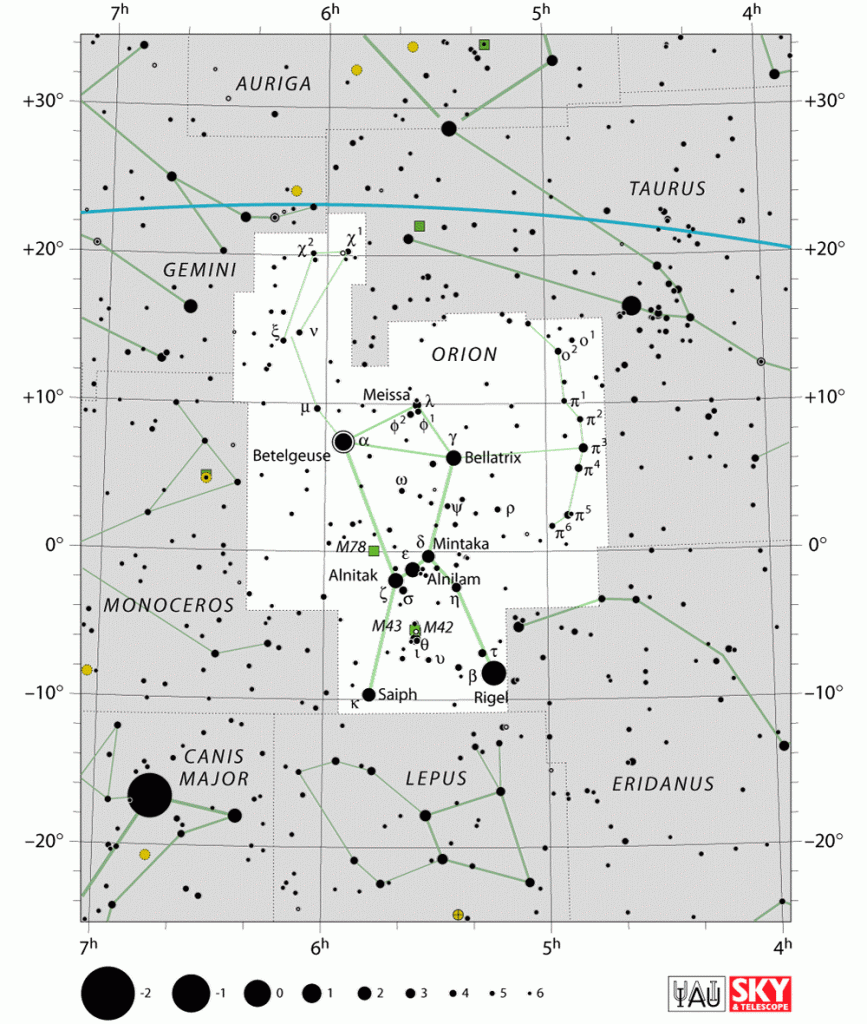
The vast expanse of the night sky, with its twinkling tapestry of stars, has captivated humanity for millennia. Across cultures and civilizations, people have looked to the stars for guidance, inspiration, and understanding. One of the most recognizable and easily identifiable constellations in the night sky is Orion, a celestial hunter forever etched in the celestial tapestry. This iconic constellation serves as a gateway to understanding the broader celestial map, offering a starting point for exploring the wonders of the night sky.
Orion: A Celestial Landmark
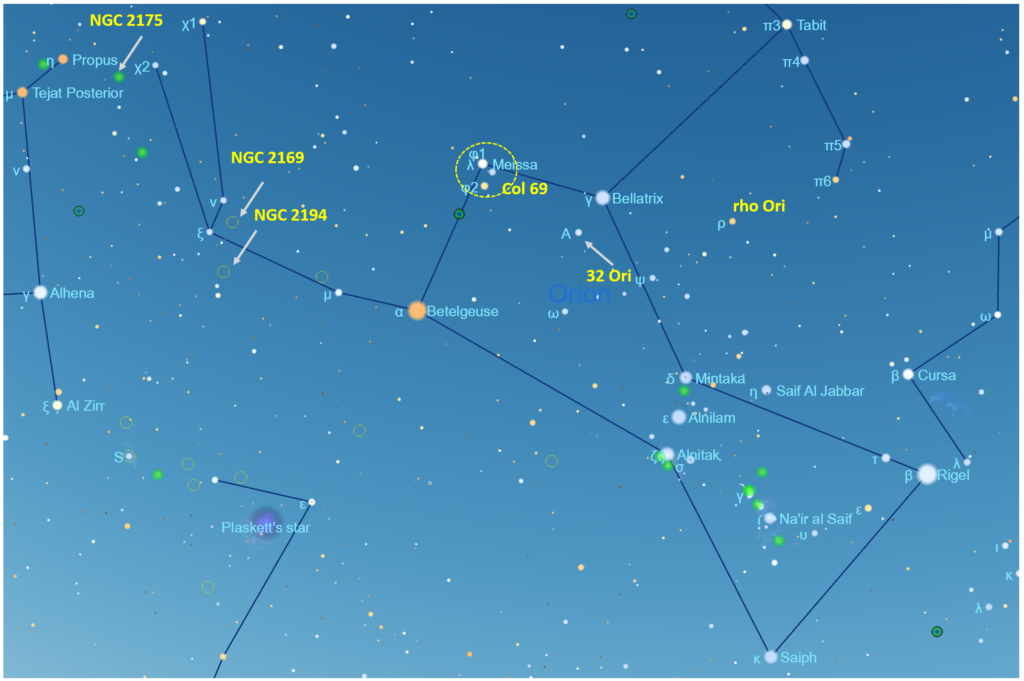
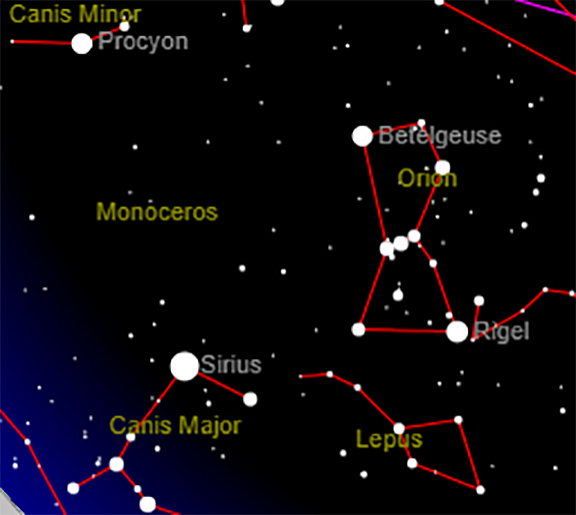
Orion is a prominent constellation easily visible from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, making it a valuable tool for navigating the night sky. Its distinctive shape, resembling a hunter with a raised club and a shield, is formed by a collection of bright stars, each with its own unique story and significance.
- Betelgeuse (α Orionis): This red supergiant star, located in Orion’s right shoulder, is one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Its reddish hue is a testament to its advanced age and impending demise as a supernova.
- Rigel (β Orionis): This blue supergiant star, found in Orion’s left foot, is the second brightest star in the constellation and one of the most luminous stars known. Its intense blue color indicates its extreme heat and youth.
- Bellatrix (γ Orionis): This blue giant star, located in Orion’s left shoulder, is known for its intense brightness and its role as a "warrior" in the constellation’s mythology.
- Mintaka (δ Orionis): This blue supergiant star, found in Orion’s belt, is a triple star system, with two of its components visible to the naked eye.
- Alnilam (ε Orionis): This blue supergiant star, also located in Orion’s belt, is one of the brightest stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
- Alnitak (ζ Orionis): This blue supergiant star, found in Orion’s belt, is a multiple star system, with a faint companion star visible in small telescopes.
- Saiph (κ Orionis): This blue supergiant star, found in Orion’s right knee, is a key component of the constellation’s iconic shape.
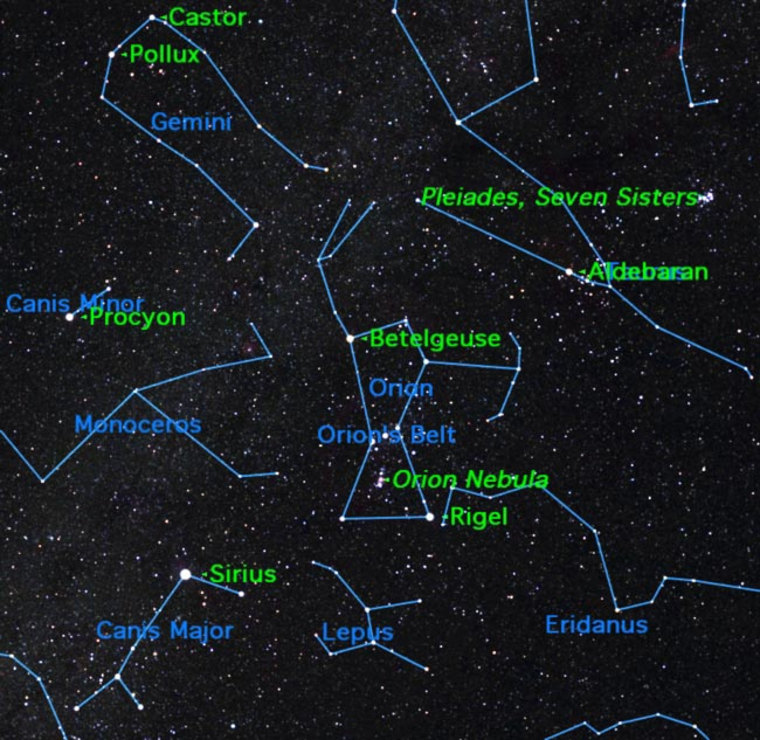
Orion: A Gateway to the Night Sky
Orion’s prominent position and easily recognizable shape make it an excellent starting point for exploring the night sky. The constellation serves as a guide to other celestial objects, including:
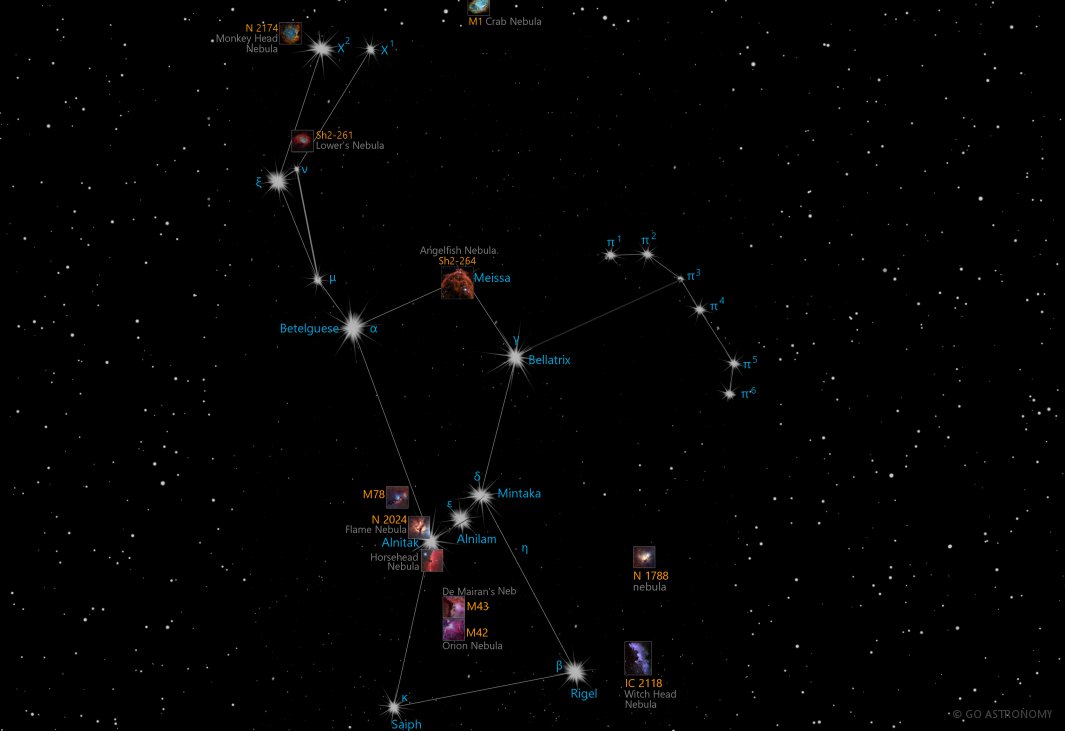
- The Orion Nebula (M42): This prominent nebula, located just south of Orion’s belt, is a stellar nursery where new stars are born. Its ethereal glow is visible to the naked eye and offers a glimpse into the processes of star formation.
- The Pleiades (M45): This open cluster of stars, located in the constellation Taurus, is visible to the naked eye and can be located by following Orion’s belt upwards towards the east.
- The Great Nebula in Andromeda (M31): This spiral galaxy, the closest major galaxy to our own Milky Way, can be found by following Orion’s belt upwards towards the north.
Orion: A Cultural and Historical Treasure
Orion’s prominence in the night sky has led to its incorporation into the mythology and folklore of numerous cultures around the world. In ancient Greece, Orion was a giant hunter who was slain by the scorpion, Scorpius. In Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with Osiris, the god of the underworld. In Chinese astronomy, Orion was known as Shen, the celestial warrior.
Orion: A Tool for Navigation and Timekeeping
Orion’s position in the night sky has also been used for navigation and timekeeping. Ancient mariners used Orion’s prominent stars to guide their ships across the seas. Farmers and astronomers used Orion’s rising and setting to track the seasons and predict agricultural cycles.
Orion: A Source of Inspiration and Wonder
The beauty and mystery of Orion have inspired poets, artists, and musicians for centuries. The constellation has been depicted in countless works of art, literature, and music. Orion’s enduring presence in human culture is a testament to its power to inspire and captivate.
Orion: A Window to the Universe
Orion’s stars offer a glimpse into the vastness and complexity of the universe. The constellation’s stars are among the brightest and most massive in the Milky Way galaxy, providing astronomers with valuable insights into the life cycles of stars and the evolution of galaxies.
Orion: A Guide to Stargazing
For those interested in exploring the night sky, Orion serves as an excellent starting point. The constellation’s prominent shape and bright stars make it easy to locate, even for novice stargazers. Once Orion is identified, it can be used as a guide to locate other celestial objects, such as the Orion Nebula, the Pleiades, and the Andromeda Galaxy.
FAQs: Orion and Stargazing
Q: What is the best time of year to see Orion?
A: Orion is visible from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, but it is most prominent in the winter months. In the Northern Hemisphere, Orion is visible from November to February. In the Southern Hemisphere, Orion is visible from May to August.
Q: How can I find Orion in the night sky?
A: Orion is easily recognizable by its distinctive shape, resembling a hunter with a raised club and a shield. The three stars that form Orion’s belt are a good starting point for locating the constellation. These stars are aligned in a straight line and point towards the east.
Q: What are some of the best telescopes for viewing Orion?
A: For observing Orion, a small telescope with a magnification of 50x to 100x is sufficient. Larger telescopes with higher magnifications can be used to view more details in the Orion Nebula and other celestial objects in the constellation.
Q: What are some of the best locations for stargazing?
A: The best locations for stargazing are typically away from city lights and other sources of light pollution. National parks, rural areas, and high-altitude locations are ideal for observing the stars.
Tips for Stargazing with Orion:
- Find a dark location: Light pollution can obscure the view of the stars. Try to find a location away from city lights and other sources of light pollution.
- Allow your eyes to adjust: It takes about 30 minutes for your eyes to adjust to the darkness. Avoid looking at bright lights during this time.
- Use a star chart or app: A star chart or a stargazing app can help you identify constellations and other celestial objects.
- Be patient: Stargazing takes time and patience. Don’t expect to see everything in one night.
- Dress warmly: The night sky can be cold, even in the summer. Dress in layers to stay warm.
- Have fun: Stargazing is a relaxing and enjoyable activity. Take your time, relax, and enjoy the view.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Orion
Orion, the celestial hunter, stands as a testament to the enduring power of the night sky to inspire and captivate. This iconic constellation, with its bright stars and celestial wonders, serves as a gateway to understanding the vastness and complexity of the universe. For those seeking to navigate the night sky, Orion offers a starting point for exploring the celestial tapestry, a journey of discovery that has captivated humanity for millennia. Whether gazing at the stars with the naked eye or through a telescope, Orion remains a source of wonder and inspiration, reminding us of our place in the vastness of the cosmos.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to the Orion Star Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!