Navigating Healthcare in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to Michigan’s Hospital Network
Related Articles: Navigating Healthcare in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to Michigan’s Hospital Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Healthcare in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to Michigan’s Hospital Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Healthcare in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to Michigan’s Hospital Network

The state of Michigan boasts a robust and diverse healthcare system, encompassing a network of hospitals, clinics, and medical centers that cater to the needs of its residents. Understanding the layout of this network is crucial for individuals seeking medical care, whether for routine checkups, specialized treatments, or emergency situations. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of Michigan’s hospital landscape, providing insights into its structure, accessibility, and the resources available to navigate this complex system effectively.
A Geographic Overview of Michigan’s Hospital Network:
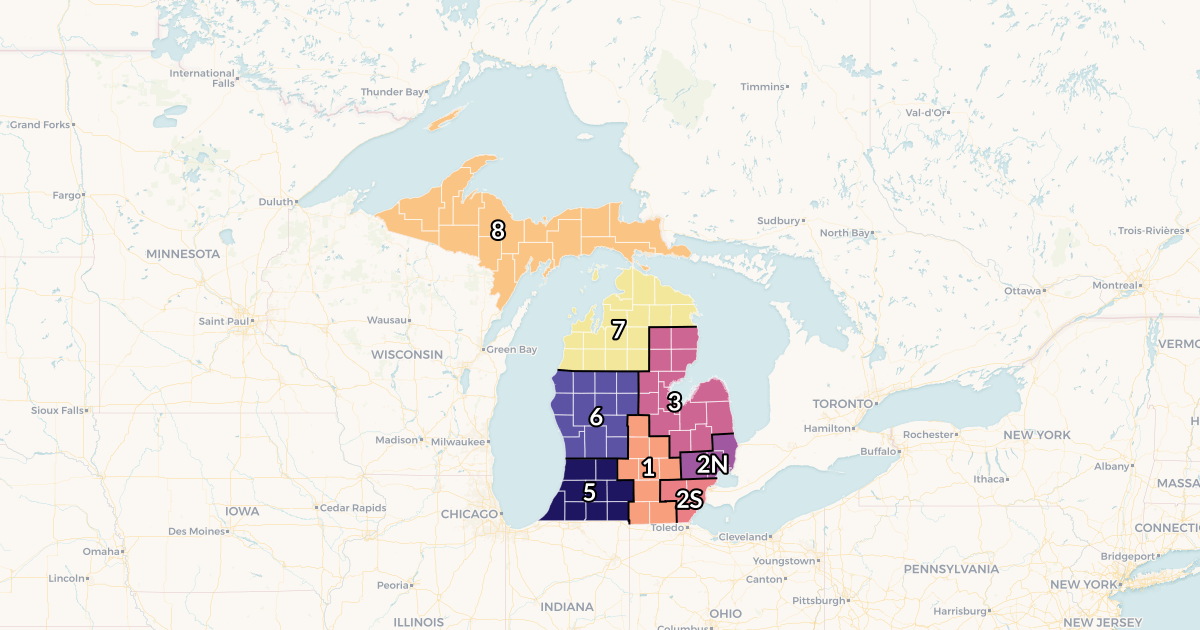
Michigan’s hospital network is geographically dispersed, reflecting the state’s diverse population distribution and its commitment to providing accessible healthcare across its various regions. Major metropolitan areas like Detroit, Grand Rapids, and Lansing house a concentration of large, multi-specialty hospitals equipped to handle complex medical cases. Smaller towns and rural communities are served by local hospitals, often specializing in primary care and general medicine.
This distribution ensures that residents have access to a hospital within a reasonable distance, regardless of their location. However, it also highlights the need for a clear understanding of the specific services offered by each facility.
Types of Hospitals in Michigan:
Michigan’s hospitals are classified based on their ownership, size, and specialization.
- Public Hospitals: Operated by state or local governments, these hospitals serve a broad range of patients, often providing care to underserved communities.
- Private Hospitals: Owned and operated by private entities, these hospitals offer a variety of services, including specialized care and advanced medical treatments.
- Academic Medical Centers: Affiliated with universities, these hospitals are renowned for their research, teaching, and advanced clinical care.
- Community Hospitals: Serving specific communities, these hospitals provide a wide range of services, including primary care, emergency services, and specialized treatments.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Hospital:
Selecting the right hospital for your needs requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Location: Proximity to your home or workplace is crucial for convenience and accessibility.
- Specialization: Hospitals may specialize in specific areas of medicine, such as cardiology, oncology, or pediatrics.
- Services Offered: Ensure the hospital provides the specific services you require, including diagnostic tests, treatments, and surgical procedures.
- Reputation: Research the hospital’s reputation, including patient satisfaction ratings, accreditation status, and clinical outcomes.
- Insurance Coverage: Confirm that your insurance plan covers the hospital you choose.
Utilizing Online Resources for Hospital Information:
The internet offers a wealth of information on Michigan’s hospitals, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare:
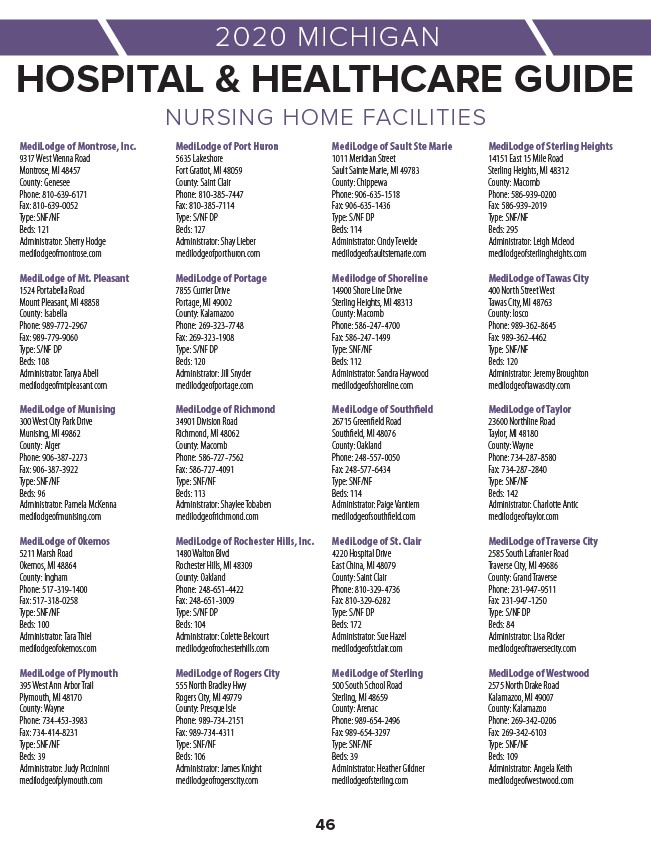
- Hospital Websites: Most hospitals have comprehensive websites that provide details about their services, staff, accreditations, and contact information.
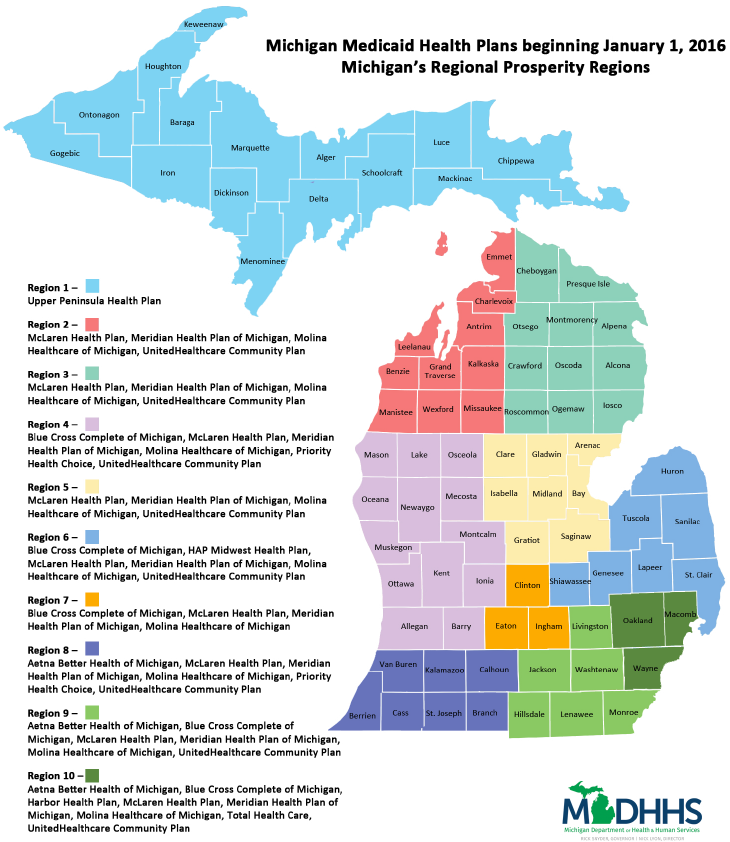
- State Health Department Websites: The Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS) website offers information on hospitals, including licensing, accreditation, and quality measures.
- Health Information Websites: Websites like Healthgrades and U.S. News & World Report provide hospital rankings, patient reviews, and information on specific medical conditions.
Navigating Emergency Situations:
In emergencies, time is of the essence. The Michigan Department of Health and Human Services offers a comprehensive list of hospitals and their emergency services on its website. Additionally, the 911 emergency service system will direct you to the nearest appropriate medical facility.
Beyond Physical Location: The Importance of Telehealth:
The advancement of technology has revolutionized healthcare delivery, with telehealth services offering remote consultations and virtual care. This allows individuals to access medical expertise from the comfort of their homes, particularly beneficial for those in remote areas or with limited mobility.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals with Knowledge:
Understanding the structure and resources of Michigan’s hospital network is crucial for navigating the healthcare system effectively. By leveraging online resources, carefully considering the factors involved in hospital selection, and utilizing telehealth services when appropriate, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare needs, ensuring access to quality medical care.
FAQs about Michigan Hospitals:
Q: How do I find a specific hospital in Michigan?
A: Utilize online resources such as Google Maps, the MDHHS website, or hospital websites to search for specific hospitals by name, location, or specialization.
Q: What are the accreditation standards for Michigan hospitals?
A: Michigan hospitals are typically accredited by organizations such as The Joint Commission (TJC) and the Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program (HFAP). These organizations set rigorous standards for quality care, patient safety, and operational efficiency.
Q: How can I find information about a hospital’s patient satisfaction ratings?
A: Websites like Healthgrades and U.S. News & World Report provide patient satisfaction ratings based on surveys conducted with patients who have received care at specific hospitals.
Q: What are the key differences between public and private hospitals in Michigan?
A: Public hospitals are typically operated by government entities and serve a broader population, often providing care to underserved communities. Private hospitals are owned and operated by private entities and offer a wider range of services, including specialized care and advanced medical treatments.
Q: How can I ensure my insurance plan covers the hospital I choose?
A: Contact your insurance provider to confirm the hospitals within your network and the coverage provided for specific services.
Tips for Navigating Michigan’s Hospital Network:
- Develop a Healthcare Plan: Create a list of preferred hospitals and healthcare providers for various medical needs.
- Maintain a Health Record: Keep a comprehensive record of your medical history, medications, and allergies for easy reference.
- Utilize Telehealth: Explore telehealth services for convenient and remote access to healthcare professionals.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check hospital websites and health information websites for updates on services, accreditations, and patient satisfaction ratings.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about your care, treatment options, and costs.
Conclusion:
Michigan’s hospital network is a vital component of the state’s healthcare system, providing a diverse range of services to its residents. By understanding the structure, accessibility, and resources available within this network, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare, ensuring access to quality medical care and a positive experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Healthcare in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to Michigan’s Hospital Network. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!