Mapping the Black Death: Understanding the Spread of the Bubonic Plague
Related Articles: Mapping the Black Death: Understanding the Spread of the Bubonic Plague
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Black Death: Understanding the Spread of the Bubonic Plague. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Black Death: Understanding the Spread of the Bubonic Plague

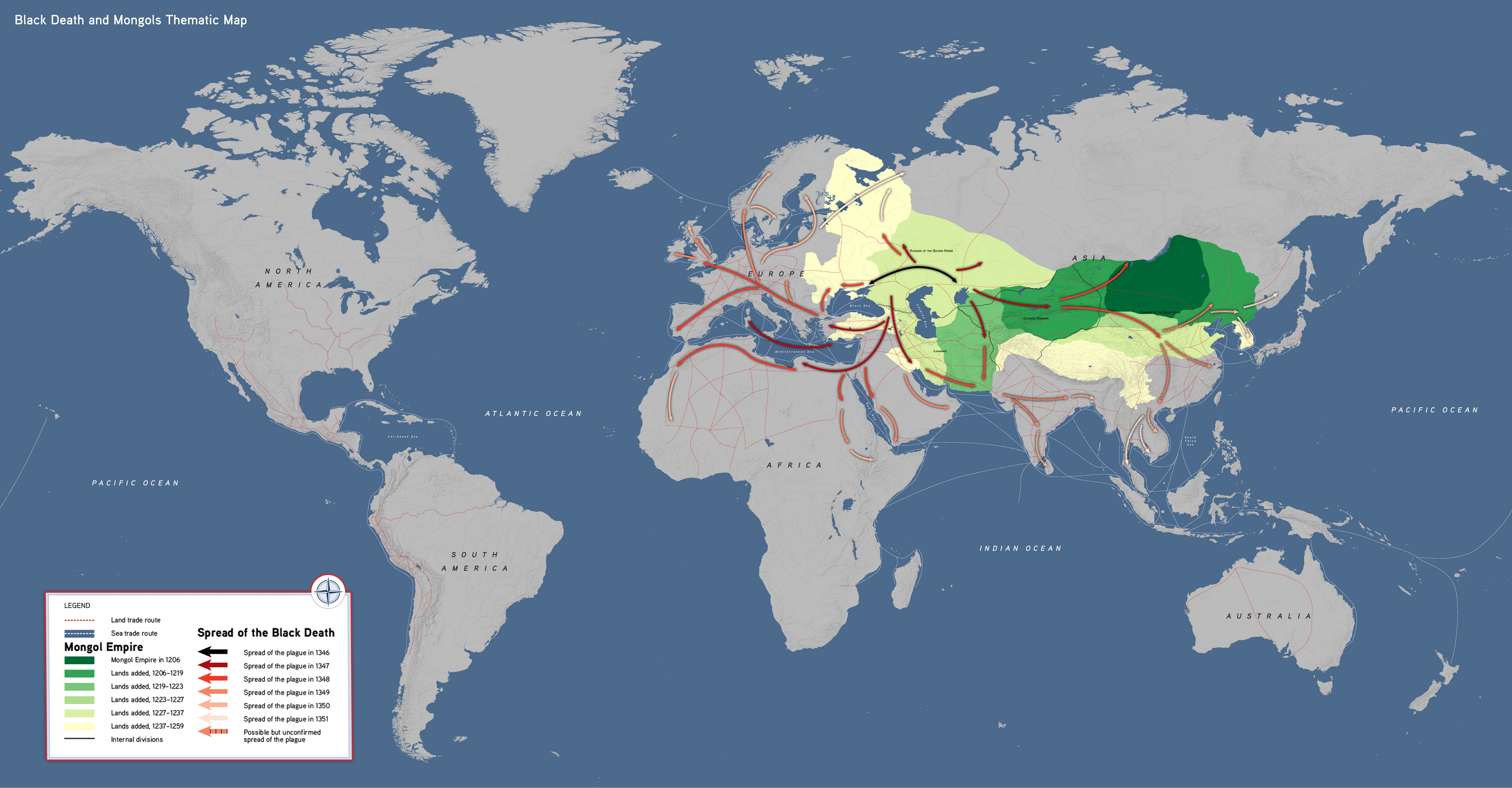
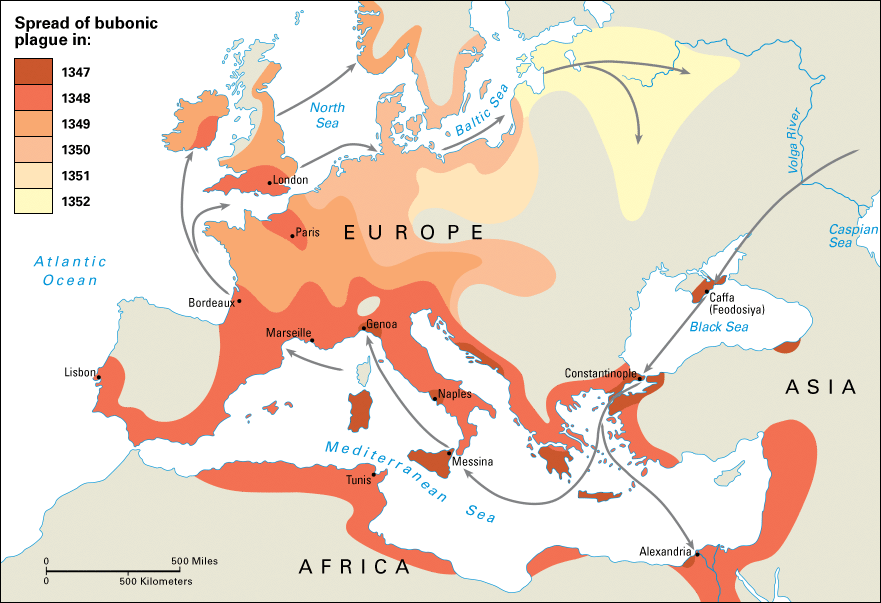
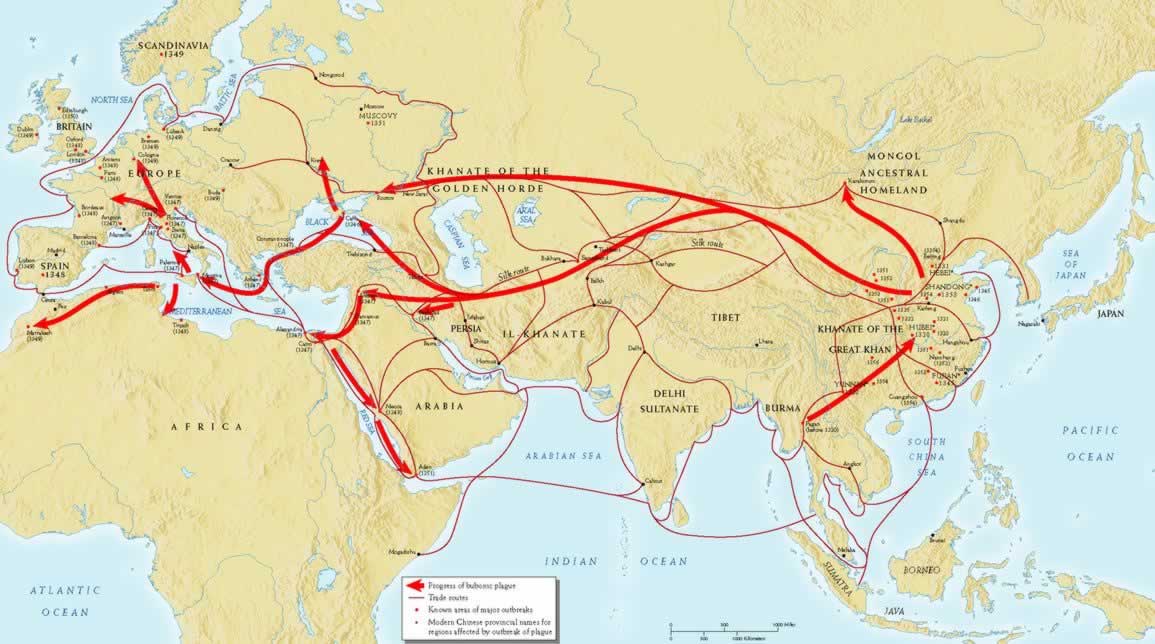
The bubonic plague, a devastating bacterial infection spread by fleas, has left an indelible mark on human history. While the infamous Black Death of the 14th century claimed millions of lives, the disease continues to exist in various parts of the world today. Understanding its spread, however, requires more than just historical accounts. Maps play a crucial role in visualizing the geographical patterns of plague outbreaks, offering valuable insights into the disease’s transmission and potential future threats.
The Power of Visualization: Mapping Plague Outbreaks
Plague maps serve as powerful tools for researchers, public health officials, and historians alike. They provide a visual representation of the disease’s trajectory, highlighting areas of high prevalence and identifying potential hotspots. By analyzing the spatial distribution of plague cases, experts can gain a deeper understanding of:
- Transmission pathways: Mapping plague outbreaks reveals the routes taken by infected individuals, animals, and vectors like fleas. This information helps identify potential transmission corridors and inform strategies for disease control.
- Environmental factors: Plague outbreaks are often linked to specific environmental conditions, such as rodent populations and climate patterns. Maps can help identify areas with suitable environments for plague transmission, facilitating early warning systems and targeted interventions.
- Historical trends: By mapping past outbreaks, researchers can track the evolution of the disease over time, identifying patterns of recurrence and potential triggers for future outbreaks. This historical perspective provides valuable insights into the disease’s long-term behavior and informs strategies for preparedness.
- Public health response: Mapping plague outbreaks allows health authorities to allocate resources effectively, target public health interventions, and monitor the effectiveness of control measures. This data-driven approach is crucial for minimizing the impact of future outbreaks.
Historical Perspectives: Mapping the Black Death
The Black Death, which ravaged Europe in the mid-14th century, serves as a stark reminder of the devastating potential of the bubonic plague. While precise data on the plague’s spread is limited, historical records and surviving maps offer valuable glimpses into its trajectory.
Early maps, often referred to as "plague maps," depicted the disease’s spread across Europe, highlighting key cities and regions affected by the outbreak. These maps, while rudimentary in their detail, provided crucial information for understanding the disease’s geographic spread and potential routes of transmission.
Modern Mapping: Tracking Plague in the 21st Century
In the 21st century, advanced technology has revolutionized the way we map and understand the bubonic plague. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing techniques allow for the creation of highly detailed and interactive maps, providing real-time information on plague outbreaks and their associated factors.
These modern maps incorporate data from various sources, including:
- Case reports: Data on confirmed plague cases, including location, date of onset, and clinical presentation, is essential for tracking the disease’s spread and identifying potential outbreaks.
- Environmental data: Factors such as climate patterns, rodent populations, and land use can influence plague transmission. Incorporating this data into maps helps identify areas at risk and inform public health strategies.
- Genetic analysis: Modern techniques allow for the genetic analysis of plague bacteria, providing valuable insights into the disease’s evolutionary history and potential for emergence of new strains. This information can be integrated into maps to track the spread of specific genetic lineages and inform targeted interventions.
The Importance of Transparency and Collaboration
Accurate and timely mapping of plague outbreaks is crucial for effective disease control. This requires transparency and collaboration among researchers, public health officials, and governments. Sharing data and resources facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s spread and enables the development of effective interventions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Plague Mapping
Q: What are the benefits of mapping plague outbreaks?
A: Mapping plague outbreaks provides valuable insights into the disease’s spread, transmission pathways, and environmental factors influencing its occurrence. This information helps inform public health interventions, resource allocation, and disease control strategies.
Q: How are modern plague maps created?
A: Modern plague maps are created using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and incorporate data from various sources, including case reports, environmental data, and genetic analysis.
Q: What are the challenges associated with mapping plague outbreaks?
A: Challenges include data availability and quality, particularly in remote or resource-limited areas. Additionally, the complex interplay of factors influencing plague transmission requires a multifaceted approach to mapping and analysis.
Tips for Understanding and Using Plague Maps
- Consider the data source: Ensure the map’s data is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date.
- Pay attention to scale: Understand the geographic scope of the map and the level of detail provided.
- Interpret the data: Understand the symbols, colors, and other visual elements used to represent plague cases and related information.
- Look for patterns: Identify areas of high prevalence, potential transmission corridors, and environmental factors associated with outbreaks.
- Stay informed: Regularly check for updates on plague outbreaks and related maps to stay informed about potential risks.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of Mapping Plague
Mapping plague outbreaks remains a crucial tool for understanding, controlling, and ultimately preventing this devastating disease. By leveraging the power of visualization, researchers, public health officials, and policymakers can gain a deeper understanding of the disease’s dynamics, identify areas at risk, and implement effective interventions to protect human health. As we continue to learn more about the bubonic plague and its complex interplay with the environment, mapping will continue to play a vital role in safeguarding our future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Black Death: Understanding the Spread of the Bubonic Plague. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!