Demystifying the ATU Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data
Related Articles: Demystifying the ATU Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the ATU Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the ATU Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data

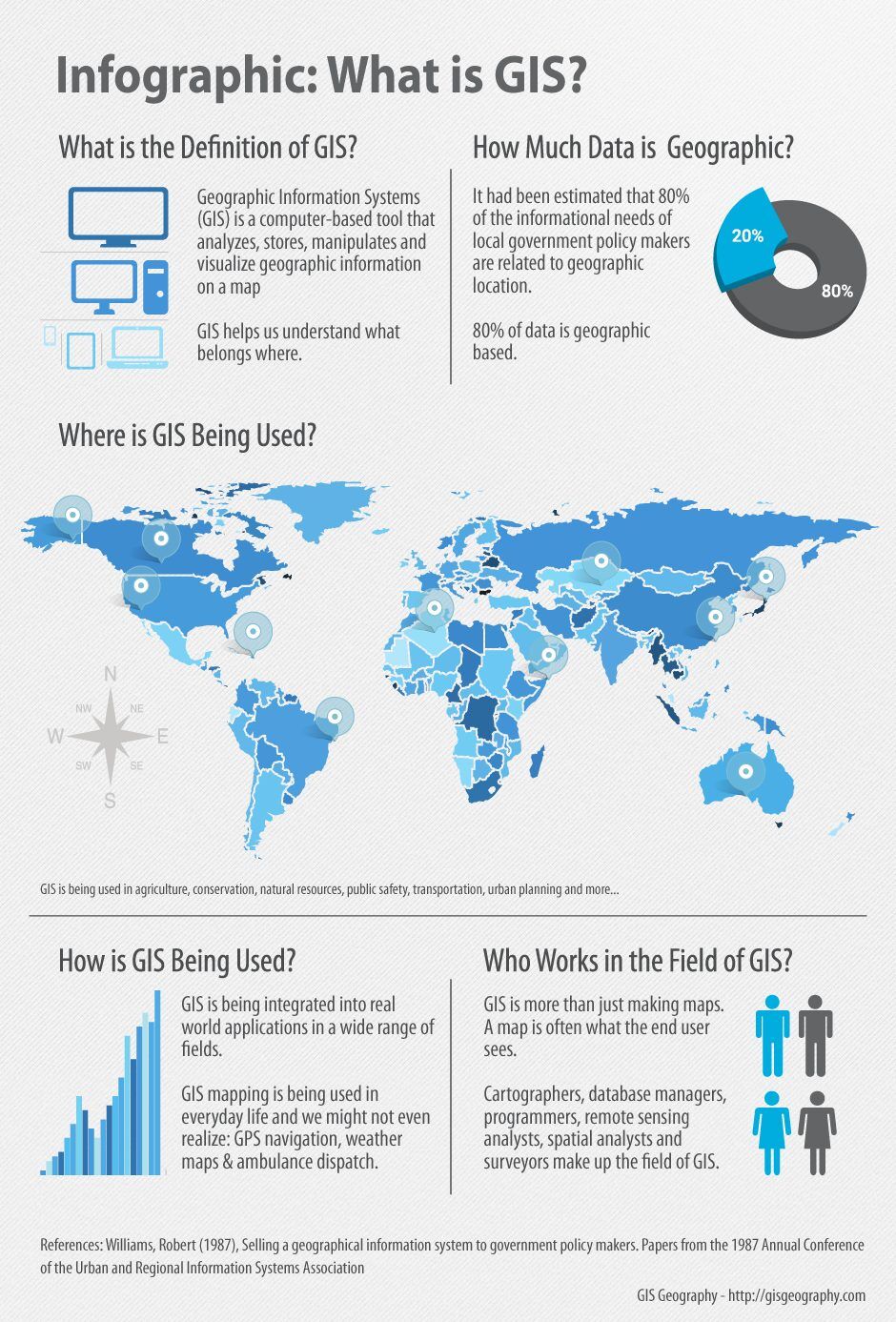
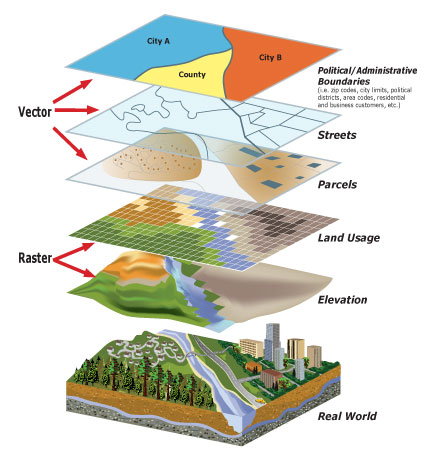
The ATU map, or Area Type Unit map, is a powerful tool used in various fields to analyze and understand geographic data. It provides a standardized system for classifying and organizing geographic areas, enabling researchers, policymakers, and businesses to gain valuable insights into population distribution, economic activity, and other crucial factors. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the ATU map, exploring its structure, applications, and significance in modern data analysis.
Understanding the ATU Map: A Framework for Geographic Data
The ATU map is a hierarchical system that categorizes geographic areas based on their characteristics and functions. It is a standardized framework developed by the European Commission, with the aim of providing a consistent and comparable system for data collection and analysis across different countries within the European Union.
Structure of the ATU Map
The ATU map consists of multiple levels, each representing a different scale of geographic aggregation. These levels are:
- Level 0: Country: This is the highest level and represents the entire geographic area of a country.
- Level 1: NUTS 1: This level divides the country into large regions, typically based on administrative boundaries.
- Level 2: NUTS 2: This level further subdivides the NUTS 1 regions into smaller sub-regions.
- Level 3: NUTS 3: This level represents the smallest administrative units within a country, often corresponding to counties or districts.
- Level 4: LAU: This level represents local administrative units, such as municipalities or cities.
- Level 5: Other: This level encompasses other geographic units that may not fit into the standard NUTS or LAU classifications, such as urban areas or functional regions.
Applications of the ATU Map: A Versatile Tool for Data Analysis
The ATU map has a wide range of applications, including:
- Population Studies: The map can be used to analyze population distribution, demographics, and migration patterns at different geographic scales.
- Economic Analysis: By combining ATU data with economic indicators, researchers can study regional economic activity, growth trends, and disparities.
- Environmental Monitoring: The map facilitates the analysis of environmental data, such as air pollution, water quality, and land use patterns.
- Social Research: ATU data can be used to study social phenomena, such as poverty, education levels, and access to healthcare.
- Urban Planning: The map provides valuable insights for urban planners, allowing them to analyze urban growth, infrastructure development, and service provision.
- Marketing and Business Strategy: Companies can utilize ATU data to understand customer demographics, market potential, and target their marketing campaigns effectively.
Benefits of Using the ATU Map: A Standardized and Consistent Approach
The ATU map offers several key benefits for researchers, policymakers, and businesses:
- Standardization: The map provides a standardized system for classifying geographic areas, ensuring consistency across different studies and projects.
- Comparability: By using the same classification system, data can be easily compared across different countries and regions.
- Accuracy: The map utilizes official administrative boundaries, ensuring accurate geographic representation.
- Accessibility: ATU data is freely available, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Flexibility: The hierarchical structure of the map allows for analysis at different scales of geographic aggregation.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the ATU map offers numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge potential limitations:
- Dynamic Boundaries: Administrative boundaries can change over time, requiring updates to the ATU map.
- Data Availability: Data availability may vary across different countries and regions, impacting the comprehensiveness of analysis.
- Granularity: The level of detail provided by the ATU map may not always be sufficient for specific research questions.
- Cultural Context: The map may not fully capture the nuances of local cultural and social factors.
FAQs on the ATU Map:
Q: What is the difference between NUTS and LAU levels?
A: NUTS levels represent larger administrative units, typically based on regions or provinces, while LAU levels represent smaller administrative units, such as municipalities or cities.
Q: How can I access ATU data?
A: ATU data is freely available from various sources, including Eurostat, the official statistics portal of the European Union.
Q: Is the ATU map applicable outside the European Union?
A: While the ATU map is primarily used within the European Union, similar geographic classification systems exist in other parts of the world.
Q: How often is the ATU map updated?
A: The ATU map is regularly updated to reflect changes in administrative boundaries and data availability.
Tips for Utilizing the ATU Map:
- Understand the Level of Detail: Select the appropriate level of geographic aggregation based on the research question or analysis objective.
- Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data used in conjunction with the ATU map.
- Contextualization: Consider the specific context of the study area when interpreting ATU data.
- Visualization: Utilize maps and other visualization techniques to effectively communicate findings based on ATU data.
- Collaboration: Engage with experts in relevant fields to ensure proper interpretation and application of ATU data.
Conclusion:
The ATU map is a powerful tool for analyzing and understanding geographic data. Its standardized framework, hierarchical structure, and widespread availability make it a valuable resource for researchers, policymakers, and businesses. By understanding the intricacies of the ATU map, users can leverage its potential to gain valuable insights into population distribution, economic activity, environmental trends, and other crucial factors, contributing to informed decision-making and effective policy development. As technology advances and data collection methods evolve, the ATU map will continue to play a vital role in our understanding and analysis of the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the ATU Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!