A Journey Through Time: Exploring Europe in the Year 800
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring Europe in the Year 800
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring Europe in the Year 800. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring Europe in the Year 800

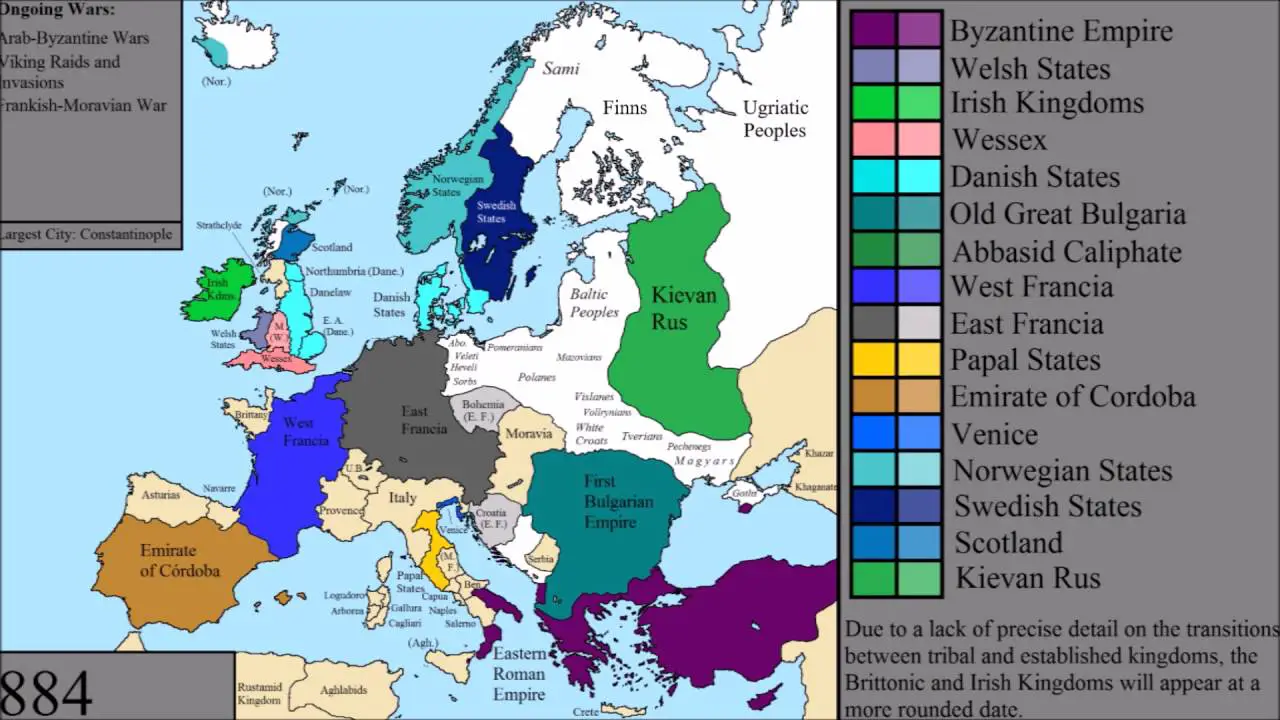
The year 800 AD marks a pivotal moment in European history, a time of transition from the late Roman Empire to the early Middle Ages. Understanding the political landscape of Europe during this period requires a deep dive into the geographical and political realities of the time. This exploration, facilitated by a map of Europe in 800, offers a unique window into the past, revealing the complex tapestry of kingdoms, empires, and cultural influences that shaped the continent.
Delving into the Map: A Visual Guide to the 9th Century
A map of Europe in 800 AD reveals a continent vastly different from the modern landscape. The Roman Empire, once a dominant force, had fragmented, leaving behind a patchwork of kingdoms and territories. The Frankish Empire, under the rule of Charlemagne, held a prominent position in Western Europe, stretching from present-day France and Germany to parts of Italy and Spain.
Key Features of the Map:
- The Frankish Empire: Charlemagne’s reign marked a period of expansion and consolidation, with the Frankish Empire encompassing much of Western Europe. The map showcases the vastness of Charlemagne’s domain, extending from the North Sea to the Mediterranean.
- The Byzantine Empire: In the east, the Byzantine Empire, heir to the Roman legacy, continued to thrive. The map highlights its strategic location, spanning the Balkans and Anatolia, serving as a bridge between Europe and Asia.
- The Rise of Islamic Influence: The Islamic conquests of the 7th and 8th centuries had a profound impact on the Mediterranean region. The map reveals the presence of the Umayyad Caliphate in Iberia and the growing influence of Islam in North Africa.
- The Norse Expansion: The Vikings, known for their seafaring skills, were actively exploring and settling territories in Northern Europe. The map showcases their presence in Scandinavia, as well as their raids on coastal areas of Western Europe.
- The Formation of New Kingdoms: The map highlights the emergence of new kingdoms, such as the Kingdom of Asturias in Spain, the Kingdom of Wessex in England, and the Kingdom of Scotland. These nascent kingdoms played a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of Europe.
The Significance of the Map:
A map of Europe in 800 AD serves as a powerful tool for understanding the historical context of the period. It provides a visual representation of:
- Political Power Dynamics: The map illustrates the distribution of power, highlighting the rise and fall of empires, the emergence of new kingdoms, and the complex interactions between various rulers.
- Cultural Exchange: The map reveals the flow of ideas, trade, and cultural influences across Europe, showcasing the interconnectedness of different regions.
- The Impact of Migration and Conquest: The map highlights the movement of people and the consequences of conquests, revealing the dynamic nature of the European landscape.
- The Foundation of Modern Europe: The map provides a starting point for understanding the origins of modern European nations and their historical relationships.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Context
While the map provides a visual representation of the political landscape, it is essential to delve deeper into the context of the period. Factors such as:
- The Carolingian Renaissance: Charlemagne’s reign witnessed a cultural revival, with renewed interest in learning and the arts. This period saw the establishment of schools, monasteries, and the promotion of literacy.
- The Role of the Church: The Catholic Church played a significant role in shaping the political and social landscape of Europe. The map highlights the influence of the Church, particularly in the Frankish Empire, where Charlemagne sought to strengthen his authority through close ties with the Papacy.
- The Viking Age: The Viking Age, spanning from the 8th to the 11th centuries, was a period of significant upheaval. The map showcases the Viking raids, their expansion into new territories, and their impact on European society.
FAQs about Europe in 800 AD:
1. What was the dominant political force in Europe in 800 AD?
The Frankish Empire, under the rule of Charlemagne, held a prominent position in Western Europe.
2. What were the main cultural influences in Europe during this period?
The period saw a blend of Roman, Germanic, and Christian influences, with the Carolingian Renaissance promoting a revival of learning and the arts.
3. What were the major challenges faced by Europe in 800 AD?
Europe faced challenges such as the decline of the Roman Empire, the rise of new kingdoms, Viking raids, and the spread of Islam in the Mediterranean region.
4. How did the map of Europe change between 800 AD and the year 1000 AD?
The map underwent significant changes, with the fragmentation of the Frankish Empire, the rise of new kingdoms, and the continued expansion of Viking influence.
5. What are the key lessons we can learn from studying the map of Europe in 800 AD?
The map offers valuable insights into the dynamic nature of power, the importance of cultural exchange, and the impact of migration and conquest on the shaping of the European continent.
Tips for Studying the Map of Europe in 800 AD:
- Focus on the key political entities: Identify the major kingdoms, empires, and territories depicted on the map.
- Consider the geographical features: Pay attention to the location of rivers, mountains, and coastlines, as they influenced trade routes and military movements.
- Examine the cultural influences: Identify areas with distinct cultural influences, such as the Byzantine Empire, the Islamic world, and the Norse settlements.
- Compare the map to modern Europe: Observe how the political boundaries and cultural landscapes have evolved over time.
- Explore primary sources: Consult historical documents, chronicles, and archaeological evidence to gain deeper insights into the period.
Conclusion:
A map of Europe in 800 AD provides a compelling glimpse into a pivotal period in European history. It reveals a continent in flux, where empires rise and fall, new kingdoms emerge, and cultural influences intertwine. By studying the map and its context, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the European landscape and the origins of modern Europe. This journey through time underscores the importance of historical perspective and the enduring power of maps to illuminate the past and inform our understanding of the present.




/Christopher-Columbus-58b9ca2c5f9b58af5ca6b758.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring Europe in the Year 800. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!